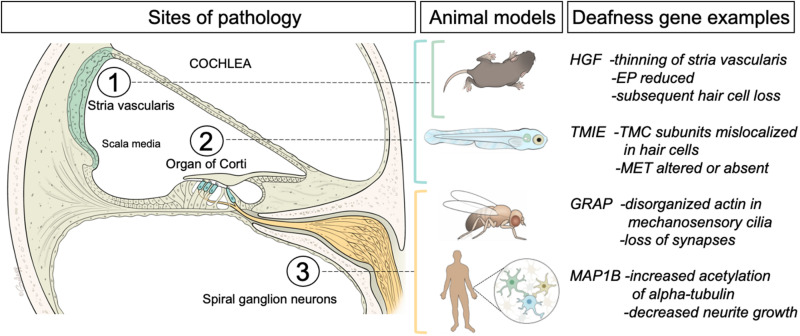
FIGURE 1.
Left panel, schematic of a cross sectional view of the cochlea, the hearing organ of the inner ear. The three regions of interest for this review are indicated. The fluid-filled middle compartment (scala media) contains the stria vascularis, a multilayer of cells (green) that generates the high concentration of potassium ions that are needed for sound detection. The neuroepithelium (organ of Corti) is comprised of sensory hair cells (inner and outer hair cells indicated in blue) embedded in a layer of supporting cells. Auditory hair cells are innervated by afferent or spiral ganglion neurons (yellow) that project to the hindbrain. Middle panel indicates the animal and cell models (Mus Musculus mice, Danio rerio zebrafish larvae, Drosophila flies, and human-derived cells) used for the studies of pathology induced by mutations in the orthologs of four different examples of human deafness genes (right panel). For a more comprehensive list of deafness genes please see the Hereditary Hearing Loss web site (https://hereditaryhearingloss.org/). A brief summary of the findings is included. EP, endocochlear potential; TMC, transmembrane channel-like; MET, mechanotransduction.