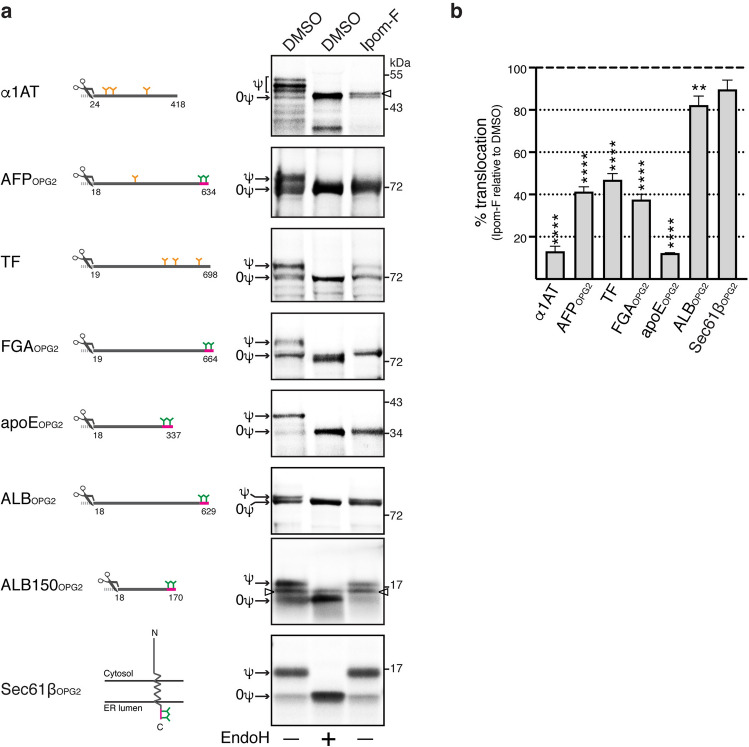
Figure 1.
Ipom-F selectively inhibits the in vitro translocation of secretory Sec61 clients. (a) α1-antitrypsin (α1AT), serotransferrin (TF) and opsin-tagged variants of α-fetoprotein (AFPOPG2), fibrinogen α-chain (FGAOPG2), apolipoprotein E (apoEOPG2), serum albumin (full-length; ALBOPG2, truncated; ALB150OPG2) and Sec61β (Sec61βOPG2) were translated in rabbit reticulocyte lysate supplemented with [35S]Met/Cys, canine rough microsomes and either DMSO or Ipom-F (1 μM). Membrane-associated products were isolated by ultracentrifugation, resolved by SDS-PAGE and analysed directly by phosphorimaging. Control samples were treated with endoglycosidase H (EndoH) to distinguish N-glycosylated (ψ) from non-glycosylated (0ψ) products. The position of a band most likely corresponding to the signal peptide (SP)-uncleaved precursor form of α1AT (see also Supplementary Fig. S1) and ALB150OPG2 is indicated with an arrowhead. Representative phosphorimaging exposures are shown (full-length gels presented in Supplementary Fig. S5). Diagrams of constructs used are shown on the left. Numbers represent the corresponding amino acids of the preprotein. The cleavage site of N-terminal signal peptides (scissors symbol) and endogenous N-glycosylation sites (orange Y symbols) are indicated. Where indicated, a 17-amino acid reporter tag (depicted in red) derived from bovine opsin was appended to the C-terminus of proteins to introduce two exogenous N-glycosylation sites (green Y symbols). (b) Quantification of the population of in vitro translated substrates from (a) that was translocated across the ER membranes following treatment with Ipom-F. Translocation efficiency was determined from the ratio of N-glycosylated to non-glycosylated form for each precursor and expressed relative to the translocation efficiency in DMSO samples (set to 100%). Values are mean ± s.e.m from at least three independent experiments. **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001 relative to DMSO (one-way ANOVA).