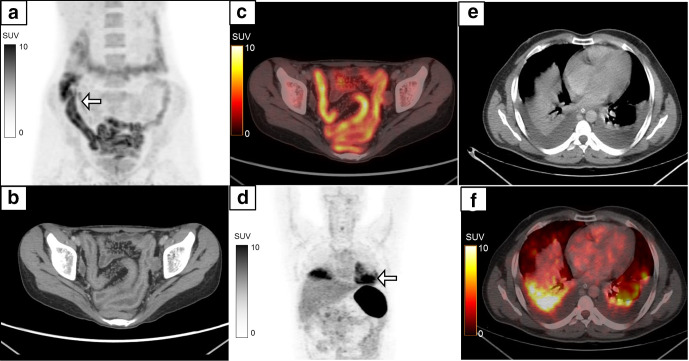
Figure 11.
False-positive 18F-FDG-labelled WBC PET/CT is seen in cases of inflammatory bowel disease which is seen in a 27-year-old female with MIP (a, white arrow) showing diffusely increased tracer uptake in the ileal loops and caecum. Transaxial CECT (b) and fused PET/CT (c) shows radiolabelled WBC accumulation (SUVmax 7.8) in the enhancing wall thickening in the distal ileal loops with increased vascularity. Biopsy from the terminal ileum revealed Crohn’s disease. Another 42-year-old male with suspected infected peri-pancreatic collection underwent 18F-FDG-labelled WBC PET/CT which showed an abnormal area of tracer activity in the lower zones of the bilateral lung fields (MIP, d, white arrow). Transaxial CT (e) and fused PET/CT (f) localized the radiolabelled WBC accumulation (SUVmax 9.7) to passive collapse in the bilateral lower lobes secondary to pleural effusion. The patient had no symptoms suggestive of any respiratory infection. CECT, contrast-enhanced CT; FDG, fluoro-D-glucose; MIP, maximum intensity projection; PET, positron emission tomography; PFN, proximal femoral nail; SUV, standardized uptake value; WBC, white blood cell.