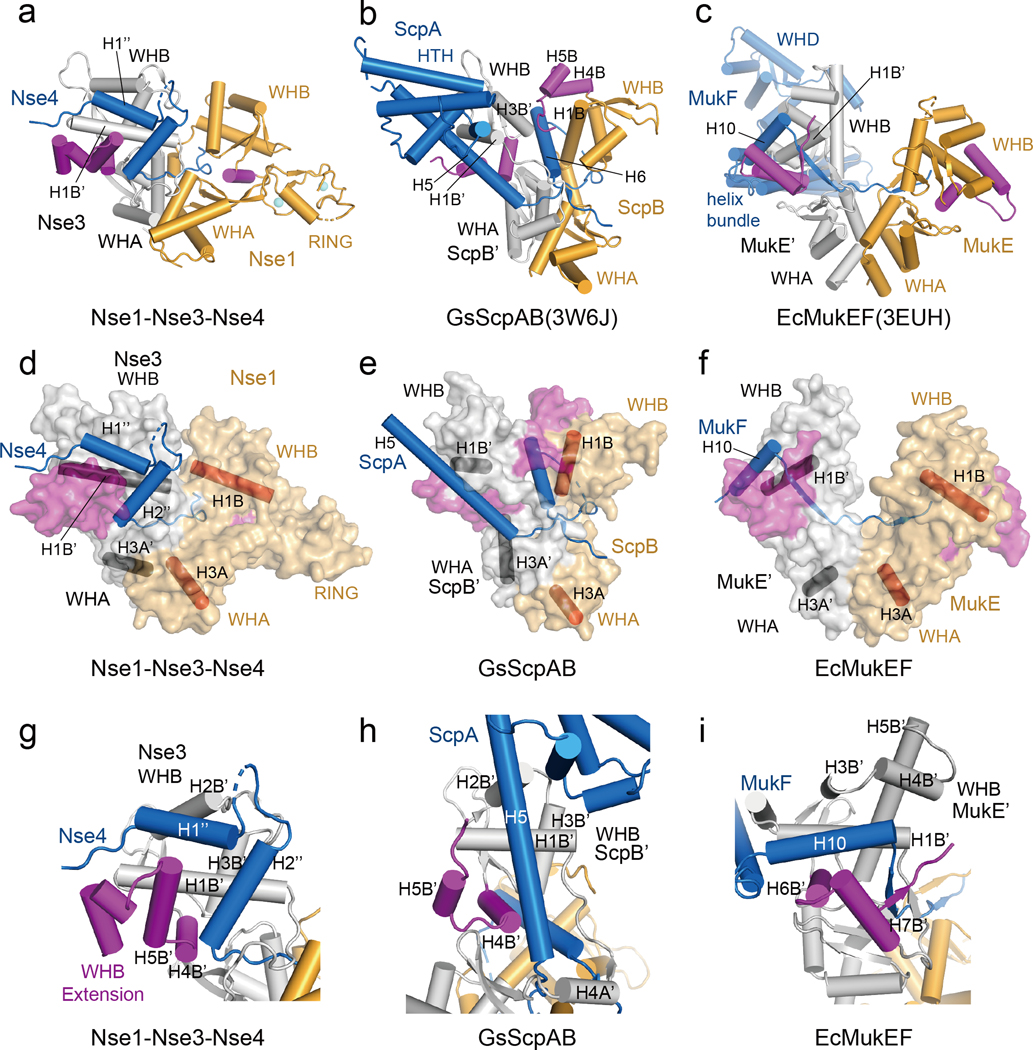
Fig. 4.
Comparison of the Nse1-3-4 complex with ScpAB and MukEF.
(a) Cylinder representation of the XlNse1 (orange)-3 (white)-4 (blue) complex. The WHB C-terminal extensions of Nse1 and Nse3 are colored in magenta.
(b) Cylinder representation of GsScpAB. The WHA of ScpB (orange) is aligned with WHA of XlNse1 in (a). The H6 helix of ScpA (blue) passes through the groove formed by ScpB (orange and magenta) and ScpB’ (white).
(c) Cylinder representation of EcMukEF. The WHA of MukE (orange) is aligned with WHA of XlNse1 in (a). MukF is colored by blue.
(d) Surface representation of the XlNse1 (light orange)-3 (white)-4 (blue) complex in same view with (a). The WHB C-terminal extensions of Nse1 and Nse3 is colored in magenta. The helices from each WH domains of Nse1 and Nse3 are shown in red and black cylinders, respectively, to represent the relative orientations of protomers and domains.
(e) Surface representation of GsScpAB in same view with (b). The helices of ScpB (light orange) and ScpB’ (white) equivalent to the helices of Nse1 and Nse3 are shown in red and black cylinder, respectively. ScpA is colored blue. The WHB C-terminal extensions of both ScpB and ScpB’ are colored magenta.
(f) Surface representation of EcMukEF in same view with (c).
(g) Close-up view of the Nse4 (blue)-Nse3 (white) interface.
(h) Close-up view of the GsScpA (blue)-ScpB’ (white) interface. The structure of the ScpB’ WHB domain is aligned with that of Nse3 in (g).
(i) Close-up view of the EcMukE’ (white)-MukF (blue) interface in same orientation as in (g).