Figure 2.
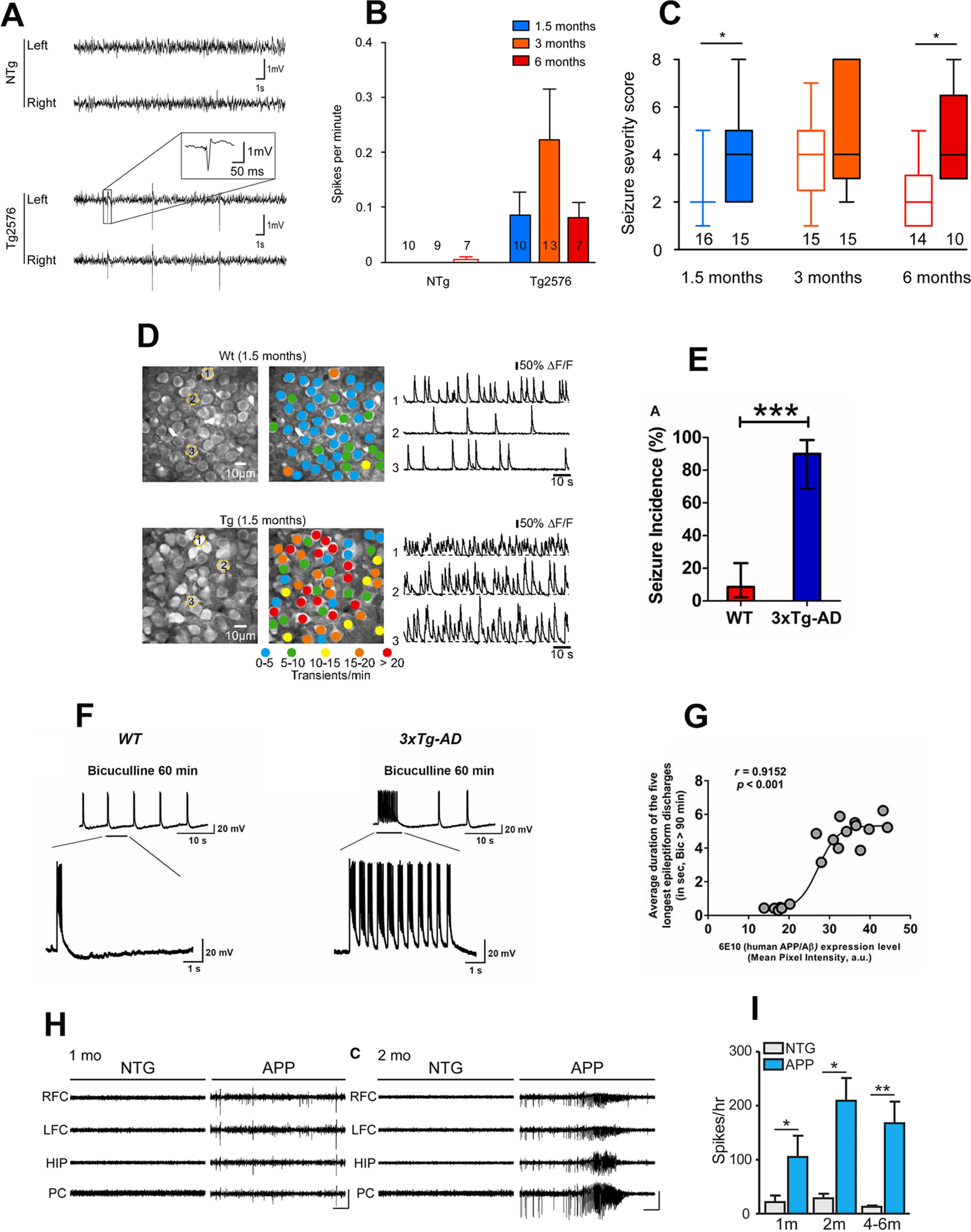
Early-onset neuronal network hyperexcitability in hAPP/Aβ mouse models of AD. A–C, Tg2576 mice exhibit spontaneous epileptiform activity and high susceptibility to pharmacologically induced seizures as young as 1.5 months of age. Reproduced with permission from Bezzina et al. (2015). A, Representative EEG traces from non-transgenic (NTg; top) and Tg2576 (bottom) mice from left and right parietal cortices. Note that only transgenic animals displayed sharp, high-voltage spikes that characterize epileptiform activity (inset). B, Quantitative analysis of the frequency of interictal spikes (mean ± SEM). Two-way ANOVA shows a significant genotype effect (p = 0.013) but no age effect (p = 0.4091) and no interaction (p = 0.3865). Numbers over the horizontal axis indicate the number of mice used in each experimental group. C, Seizure severity score of 1.5-, 3-, and 6-month-old Tg2576 male mice and NTg age-matched littermates. Whiskers boxes represent the interquartile distribution. Number of mice in each group is indicated below the boxes. Tg2576 mice exhibit more severe seizures than NTg at 1.5 and 6 months of age (Dunn’s tests: p < 0.05 for Tg2576 vs NTg at 1.5 and 6 months old). Note that only transgenic animals exhibit lethal seizures. Numbers over the horizontal axis indicate the number of mice used in each experimental group. D, Early hyperactivity of hippocampal neurons of 1.5-month-old APP23xPS45 mice (an age when no plaques are detectable). Reproduced with permission from Busche et al. (2012). Left, CA1 neurons imaged in vivo in a WT and a transgenic mouse, respectively. Center, Activity maps in which hue is determined by the frequency of spontaneous Ca2+ transients, overlaid with the anatomic image (left). Right, Spontaneous Ca2+ transients of the corresponding neurons marked (left). E–G, Early-onset seizure susceptibility and epileptiform activities in three-week-old 3xTg-AD mice (much before plaques and overt cognitive impairment). Reproduced with permission from Kazim et al. (2017). E, Incidence of convulsive seizures after audiogenic stimulation was markedly higher in three-week-old 3xTg-AD mice (blue bar) compared with WT mice (red bar). The data are presented as percent incidence with 95% confidence interval and compared using exact logistic regression stratified by litter; ***p < 0.001, compared with WT. WT (n = 35) and 3xTg-AD (n = 20) mice. F, Ictal-like epileptiform discharges in CA3 pyramidal cells of hippocampal slices from three-week-old 3xTg-AD mice. Left, CA3 intracellular recording from a WT slice after bicuculline addition (50 μm). Within 20 min, bicuculline induced rhythmic, short epileptiform discharges (≤1.5 s in duration) that were ongoing for at least 1 h of continuous recording. Membrane potential at the beginning of recording: −60 mV. Right, CA3 intracellular recording from a 3xTg-AD slice after bicuculline. Bicuculline first induced short synchronized epileptiform discharges that were similar to those in WT slices. However, continuous perfusion with bicuculline induced prolonged epileptiform (ictal-like) discharges (>1.5 s) in 3xTg-AD slice. Membrane potential at the beginning of recording: −65 mV. G, Positive correlation of intraneuronal human APP/Aβ expression in CA3 neurons and ictal-like activity in CA3 region. Correlation analyses revealed a positive relationship between intraneuronal human APP/Aβ immunoreactivity in the CA3 neurons (analyzed by 6E10, human APP/Aβ) and average duration of the five longest epileptiform discharges recorded during a 5-min period after 90 min of bicuculline application in the CA3 region of hippocampal slices from the same mice. Data from Saline-3xTg-AD (n = 9) and 6E10–3xTg-AD (n = 9) was pooled together to evaluate the correlation. The sigmoidal curve based on nonlinear regression is also shown. H, I, Early-onset epileptic activity in one- and two-month-old hAPP-J20 mice. Reproduced with permission from Fu et al. (2019). H, Representative EEG traces from NTg and hAPP-J20 mice at one and two months of age, with epileptiform spikes at one month of age and a seizure at two months of age in hAPP-J20 mice. Electrodes were in left and right frontal cortices (LFC and RFC), hippocampus (HIP), and parietal cortex (PC). Scale bars: 1 mV, 10 s. I, The number of epileptic spikes per hour in NTg or hAPP-J20 mice at one, two, and four to six months of age (n = 3−5 mice per genotype and age).
