Figure 1.
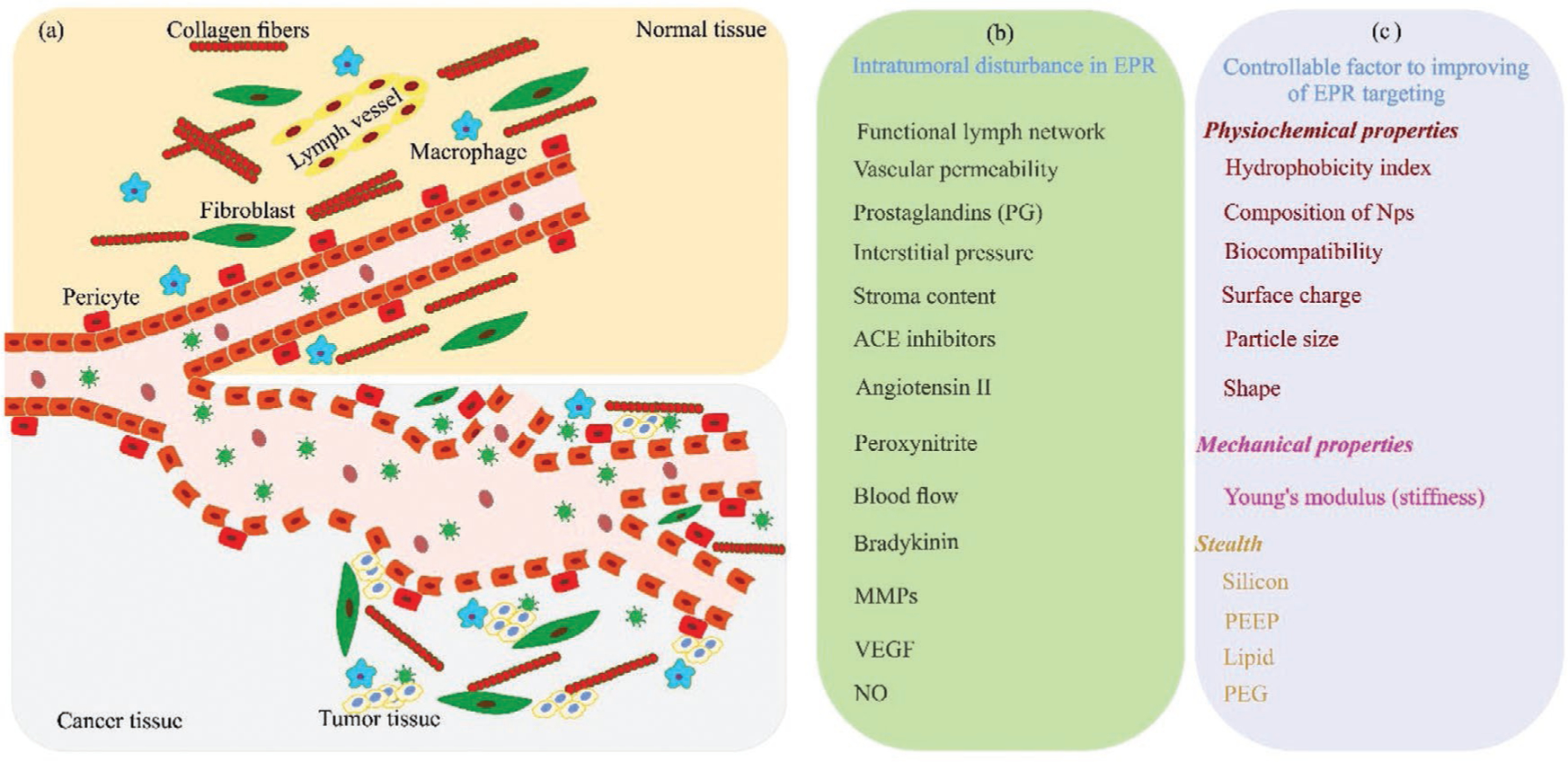
The EPR effect. a) Schematic illustration of the EPR effect in cancer and normal tissue. b) Altered tissue properties in cancerous tissue. c) Controllable factors to improve the EPR effect targeting. The stealth design of NPs aims to have maximum circulation half-life to ensure continuous delivery into the tumor site via the leaky vasculature. ACE, angiotensin-converting-enzyme; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factors; NO, nitric oxide; PEG, poly ethylene glycol; PEEP, poly (ethyl ethylene phosphate).
