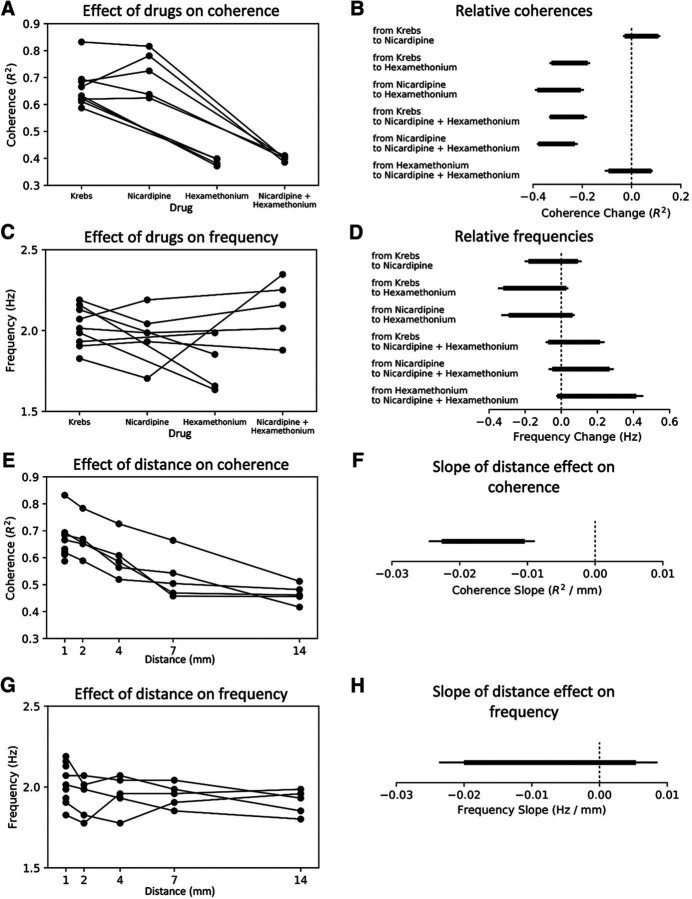
Figure 3.
A, The effect of drugs on myoelectric coherence over a distance of 1 mm. B, The associated 90% and 95% intervals of the posterior distribution (depicted as thick and thin lines, respectively) for the mean coherence in A. Myoelectric coherence in hexamethonium alone and in hexamethonium + nicardipine was significantly reduced compared with Krebs solution or nicardipine alone. There was no significant difference between Krebs solution and nicardipine alone, nor between hexamethonium alone and hexamethonium + nicardipine. C, The effect of drugs on the highest-amplitude myoelectric frequency and (D) the posterior distribution intervals. No significant differences in frequency occurred between any of the drug combinations. E, Myoelectric coherence over space (longitudinal separation of electrodes). F, The associated 90% and 95% intervals of the posterior distribution of the regression slope in E. This demonstrates a significant inverse relationship between myoelectric coherence and longitudinal distance. In comparison, there was no change in the maximum-amplitude myoelectric frequency associated with distance along the gut (G, H).