Figure 5. Changes in the right ventricular (RV) flow hemodynamic profile associated with nitric oxide challenge.
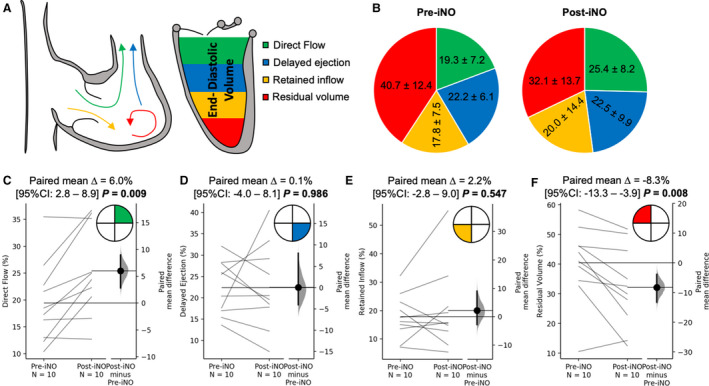
A, Graphical representation of the effect of inhaled nitric oxide (iNO) challenge on the flow components derived by 4‐dimensional–flow magnetic resonance imaging tracking, measured in the RV. B, Pie chart representation of average values of the 4 flow components at baseline and after iNO challenge. C through F, Pairwise comparison of individual flow components. There was a significant increase in direct flow (C) from baseline on iNO administration, but the opposite effect was observed in the residual volume. There were no changes in delayed ejection and retained volume.
