Figure 1. Decline in renal function with age and the effect of renal function on plasma levels of toxic metabolites of the intestinal microbiome.
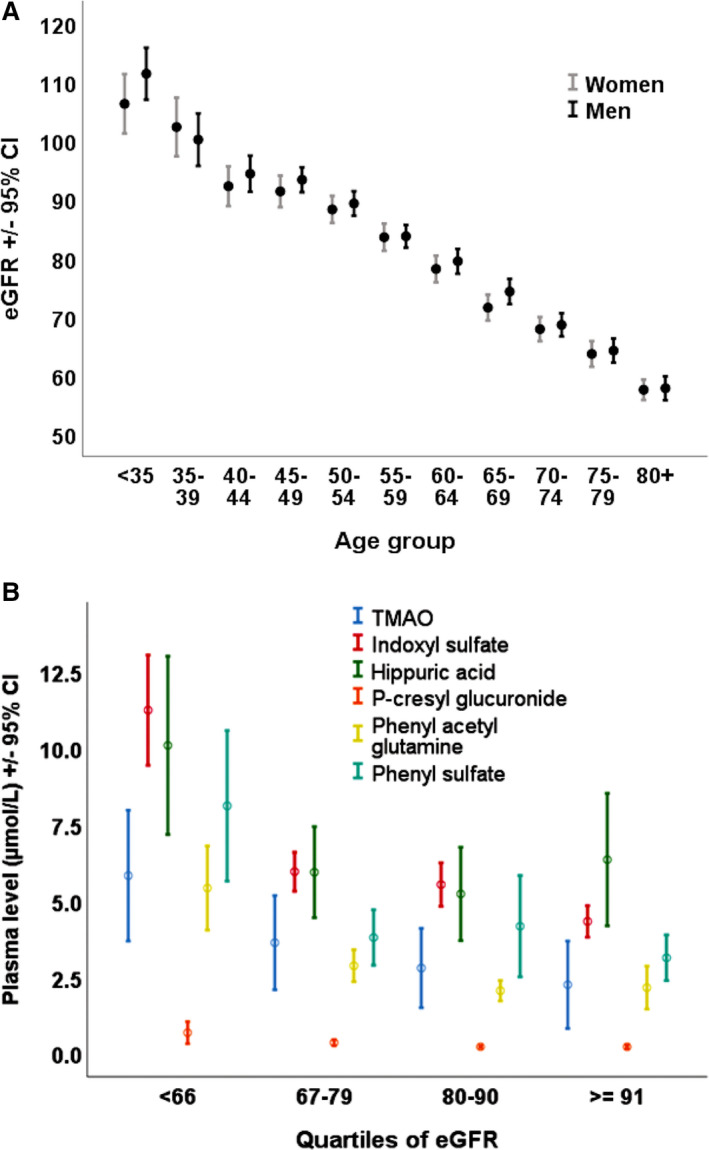
A, Decline in renal function with age. Among patients referred for stroke prevention, renal function declines linearly with age. By age 80, the mean eGFR is <60 mL/min per 1.73 m2 (n=3967). eGFR was computed using the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equations. Reprinted from Spence JD et al with permission of the publisher. Copyright © 2015 Oxford University Press. 26 B, Effect of renal function on plasma levels of toxic intestinal metabolites. Even a modest reduction of renal function to an eGFR <66 mL/min per 1.73 m2 was associated with significantly higher plasma levels of all the intestinal metabolites (analysis of variance P<0.0001 for all except 0.01 for p‐cresylglucuronide and 0.006 for phenyl sulfate). Levels of P‐cresylsulfate were also increased significantly (P<0.0001), but the levels were much higher (increasing from 30 μmol/L in the highest quartile of eGFR to 70 μmol/L in the lowest quartile), so they are omitted from this graph because of scale. eGFR indicates estimated glomerular function; and TMAO, trimethylamine n‐oxide. Reprinted from Spence et al with permission of the publisher. Copyright © 2020, Wolters Kluwer Health. 27
