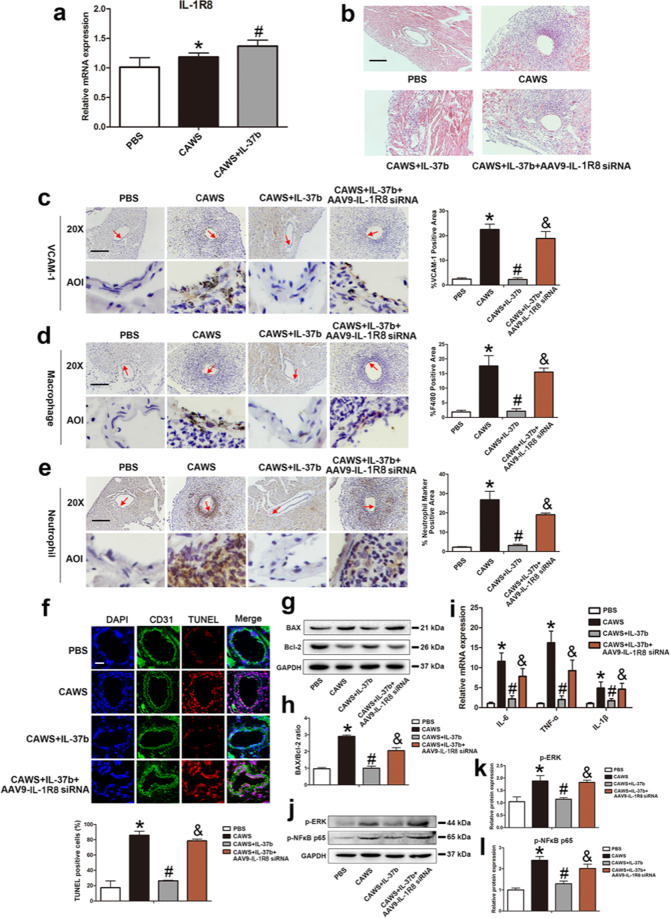
Fig. 7. Mitigation of IL-37b-mediated coronary artery endothelial cell apoptosis and inflammation was realized via IL-1R8 pathway.
a The expression of IL-1R8 were detected in the KD mouse model after IL-37b treatment (n = 6). b Effects of silencing of IL-1R8 on coronary arteritis were observed by H&E staining. Magnification: ×200. Scale bar = 100 μm. c–e The endothelial expression of VCAM-1, macrophage marker F4/80, and neutrophil marker was examined after IL-1R8 gene silencing using IHC staining. AOI were indicated with a red arrow. Scale bar = 100 μm. Right: The histograms respectively exhibited the percentage of VCAM-1, F4/80, and neutrophil marker-positive areas. Significance: *P < 0.05 vs. the PBS group, #P < 0.05 vs. the CAWS group, and &P < 0.05 vs. the CAWS + IL-37b group. f DNA fragmentation was examined using TUNEL staining. Scale bar = 100 μm. Below: Percentage of TUNEL-positive cells was shown in the histogram. Significance: *P < 0.05 vs. the PBS group, #P < 0.05 vs. the CAWS group, and &P < 0.05 vs. the CAWS + IL-37b group. g, h BAX/Bcl-2 ratio was analyzed by western blot analysis. i The mRNA expression levels of IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β were determined after silencing of IL-1R8. j–l Effects of IL-1R8 silencing on the phosphorylation level of ERK and NFκB p65 were assessed by western blotting. Significance: *P < 0.05 vs. the PBS group, #P < 0.05 vs. the CAWS group, and &P < 0.05 vs. the CAWS + IL-37b group. N = 6 mice per group, and each experiment was conducted at least three times.