FIGURE 3.
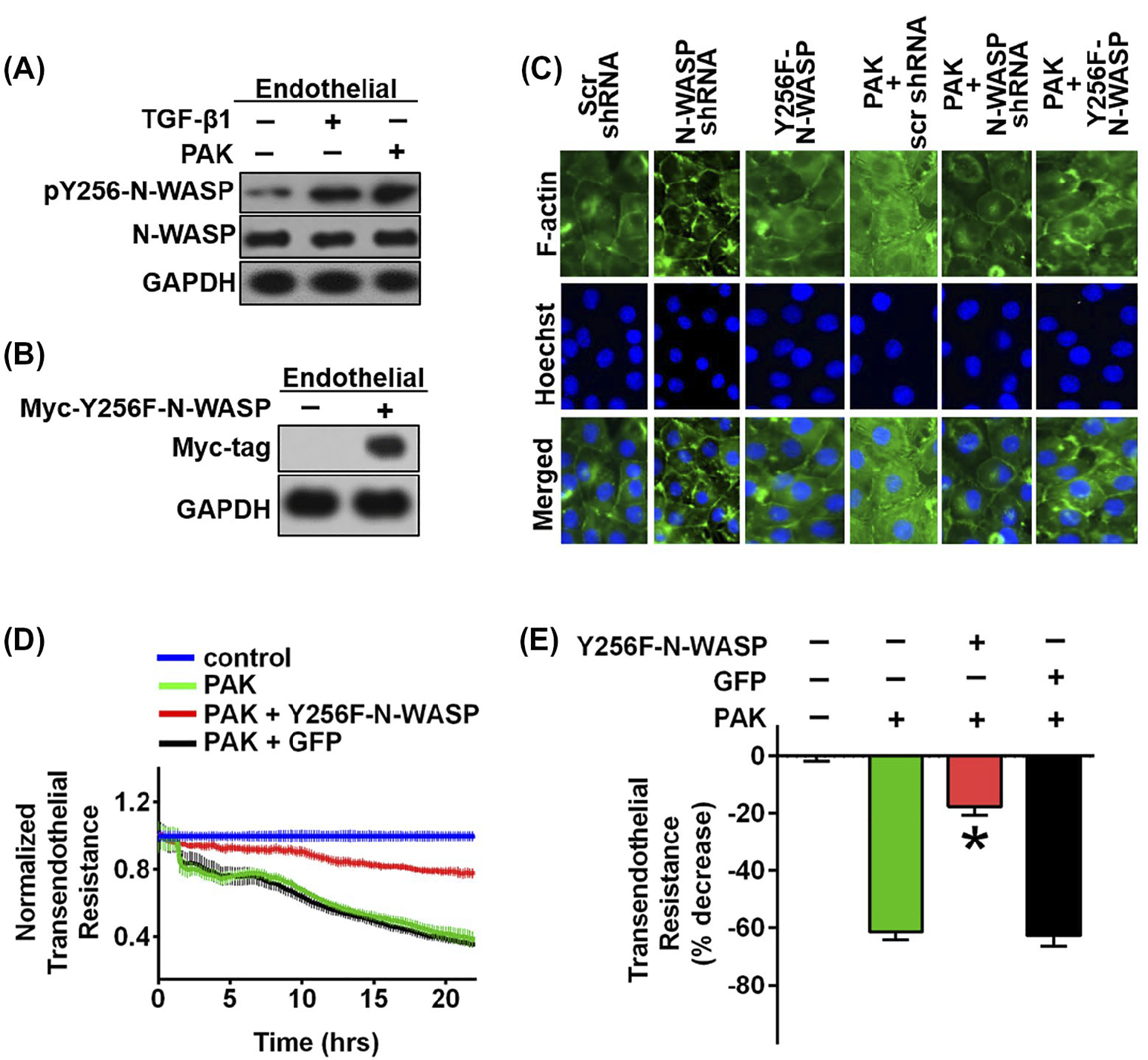
Phosphorylation of N-WASP Y256 is required for P aeruginosa induced permeability and actin stress fiber formation in RMVECs. A, Increased phosphorylation of N-WASP Y256 in response to TGF-β1 and P aeruginosa treatment in RMVEC cells. B, Forced expression of the dominant negative N-WASP mutant (myc-Y256F-N-WASP), a non-phosphorylatable mutant, in RMVEC cells. C, Expression of N-WASP mutant, myc-Y256F-N-WASP (Y256F-N-WASP), inhibited P aeruginosa induced stress fiber formation in RMVEC cells. Actin stress fibers are immunostained with phalloidin (green) and nuclei with Hoechst (blue). Representative images are showed. D, Expression of N-WASP mutant (Y256F-N-WASP) blocked P aeruginosa-induced endothelial permeability. ECIS measurement of RMVEC monolayers with or without myc-Y256F expression in response to P aeruginosa challenge (MOI = 40), electrical resistance was measured 24 h post P aeruginosa stimulation. E, Resistance value was calculated based on Figure D, 24 h post P aeruginosa stimulation. Data are presented as percentage of decreased resistance normalized to control (n = 6–8). Data are presented as means ± SEM. *P < .01
