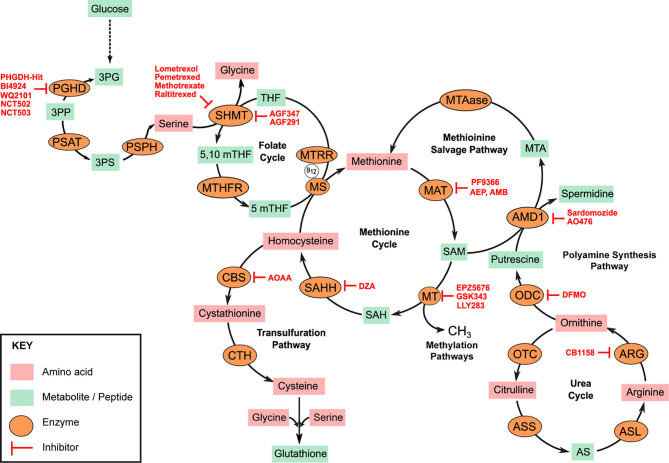
Figure 1.
Amino acid metabolic pathways. Serine, Glycine metabolic pathway represents a significant glycolysis deviation pathway in cancer. Overexpression of phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (PHGDH) drives conversion of 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG) to 3-phosphohydroxypyurvate (3PP). 3PP is aminated to 3-phosphoserine (3PS) by phosphoserine aminotransferase (PSAT). 3PP is subsequently hydrolyzed to serine by phosphoserine phosphatase (PSPH). Serine hydroxy methyltransferase (SHMT) simultaneously catalyzes the conversion of serine to glycine and tetrahydrofolate (THF) to 5,10 methyltetrahydrofolate (5,10mTHF). Methyltetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) catalyzes the reduction of 5,10mTHF to 5mTHF which is critical for the re-methylation of homocysteine to methionine by methionine synthase (MS). MS requires Vitamin B12 as cofactor which must be converted to its co-factorial form by methionine synthase reductase (MTRR). Methionine adenosyl-transferase (MAT) isoenzymes catalyze the conversion of methionine to S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) in an ATP-dependent reaction. SAM is the universal donor of methyl units to several methyl transferases (MTs) in the cell and thus regulates several methylation sensitive reactions such as DNA, RNA, or histone methylation. S-adenosyl homocysteine (SAH) is hydrolyzed to homocysteine for methionine resynthesis by SAH hydrolase (SAHH). Some homocysteine can be deviated to the transulfuration pathway for the generation of cysteine. Homocysteine is first converted to cystathionine by cystathionine beta synthase (CBS) and subsequently to cysteine by cystathionine γ-lyase (CTH). Some SAMs are deviated for the synthesis of polyamines. S-adenosyl methionine decarboxylase (AMD1) catalyzes the transfer of aminopropyl groups from SAM to putrescine to generate spermidine and 5-methionineadenosine (MTA). Methionine can be salvaged from this reaction by 5-methionineadenosine phosphorylase (MTAase). ODC, Ornithine decarboxylase; OTC, Ornithine transcarbamylase; ARG, Arginase; ASS, Argininosunicate synthase, AS, Argininosuccinate; ASL, argininosuccinate lyase. Specific enzyme inhibitors (highlighted in red) are discussed in the main text.