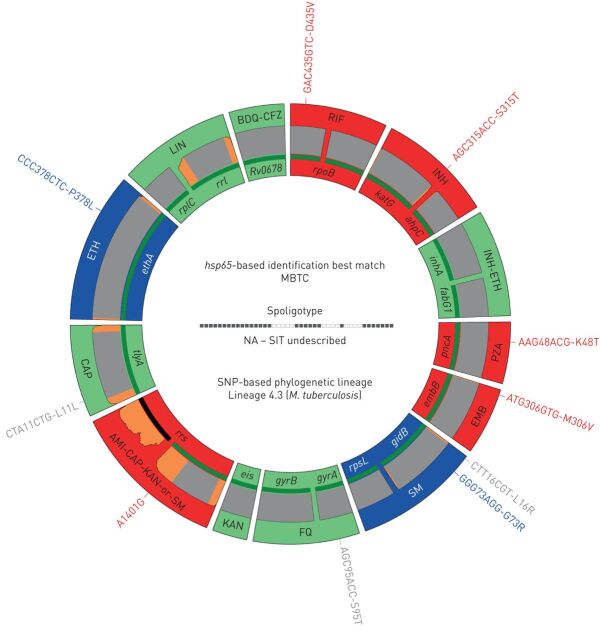
FIGURE 1.
Deeplex Myc-TB results identifying a pre-extensively drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC) strain in a sputum DNA sample collected in a tuberculosis drug resistance survey conducted in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. RIF: rifampicin; INH: isoniazid; PZA: pyrazinamide; EMB: ethambutol; SM: streptomycin; FQ: fluoroquinolones; KAN: kanamycin; AMI: amikacin; CAP: capreomycin; ETH: ethionamide; LIN: linezolid; BDQ: bedaquiline; CFZ: clofazimine; NA: not applicable; SIT: spoligotype international type; SNP: single nucleotide polymorphism; LOD: limit of detection. Information on hsp65 best-match-based identification, spoligotype (in this case, not yet known to the SITVIT database) and phylogenetic SNP-based identification of MTBC lineage is shown in the centre of circle. Information on drug susceptibility and drug resistance predictions for 13 anti-tuberculous drugs/drug classes is as follows. Target gene regions are grouped within sectors in a circular map according to the anti-tuberculous drug resistance with which they are associated. Sectors in red and green indicate targets in which resistance-associated mutations or either no mutation or only mutations not associated with resistance (shown in grey) are detected, resulting in predictions of resistant or susceptible phenotypes, respectively. Blue sectors refer to regions where as-yet uncharacterised mutations are detected. Green lines above/below gene names represent the reference sequences with coverage breadth >95%. LOD of heteroresistance (reflected by subpopulations of reads bearing a mutation) depends on the read depth at mutation position and is shown either as grey (LOD 3%) or orange zones (LOD >3–80%) above/below reference sequences. Here, LOD is >3% at the end of a few targets only and over two rrs regions with usual lower coverage.