Figure 6.
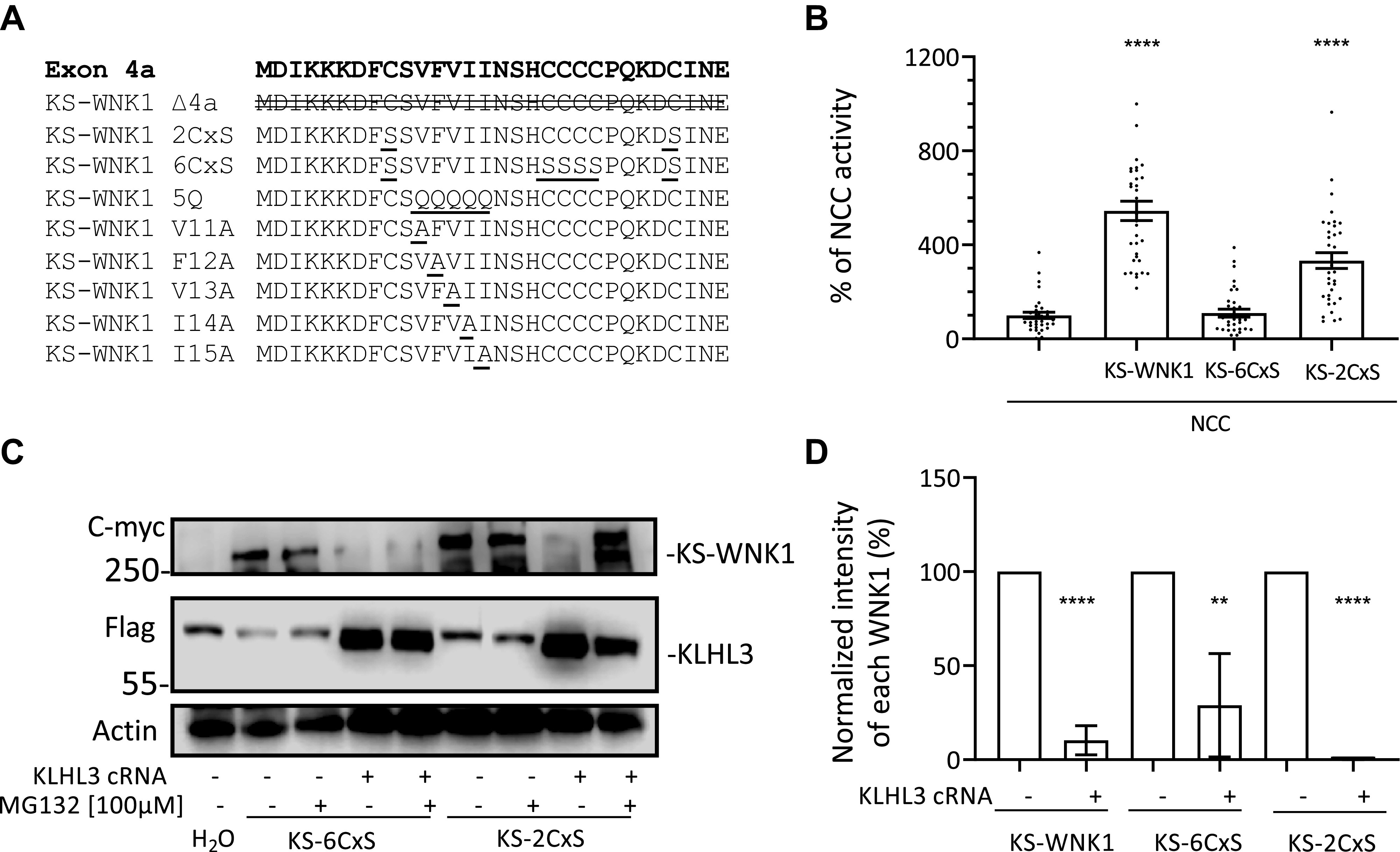
Mutation of the six conserved cysteines encoded in exon 4a impairs the ability of kidney-specific with no lysine kinase 1 (KS-WNK1) to activate NaCl cotransporter (NCC) but does not prevent cullin-3 (CUL3)-Kelch-like protein 3 (KLHL3) E3-induced degradation. A: amino acid sequence encoded by exon 4a. Different KS-WNK1 mutants were generated for this work with variations in the sequence of this region. The modifications introduced in each mutant are indicated. B: NCC was coexpressed in oocytes with KS-WNK1, KS-6CxS (in which all six cysteines were mutated to serine), or KS-2CxS (in which the two peripheral cysteines were mutated to serine). Thiazide-sensitive Na+ uptake of NCC-expressing oocytes was set to 100% and compared with all other groups, which were normalized accordingly. KS-WNK1-6CxS did not activate NCC, whereas KS-WNK1-2CxS did activate NCC, albeit at a lower level than wild-type KS-WNK1 (n = 3 transport assays, ****P < 0.0001 vs. NCC; 3 points outside graphic limits). C: representative Western blots showing the expression of KS-WNK1-6CxS and KS-WNK1-2CxS. Both mutant proteins are targeted for degradation by CUL3-KLHL3 E3, whereas treatment with MG132 could prevent KS-WNK1-2CxS degradation. D: compiled results of densitometric analysis from at least two different Western blot experiments like that presented in (B). Expression levels of KS-WNK1, KS-WNK1-6CxS, and KS-WNK1-2CxS in the absence of KLHL3 were normalized to 100% and compared with groups expressing KLHL3 (n = 2−4 Western blots, **P < 0.01 and ****P < 0.0001 vs. control without KLHL3).
