fig 1.
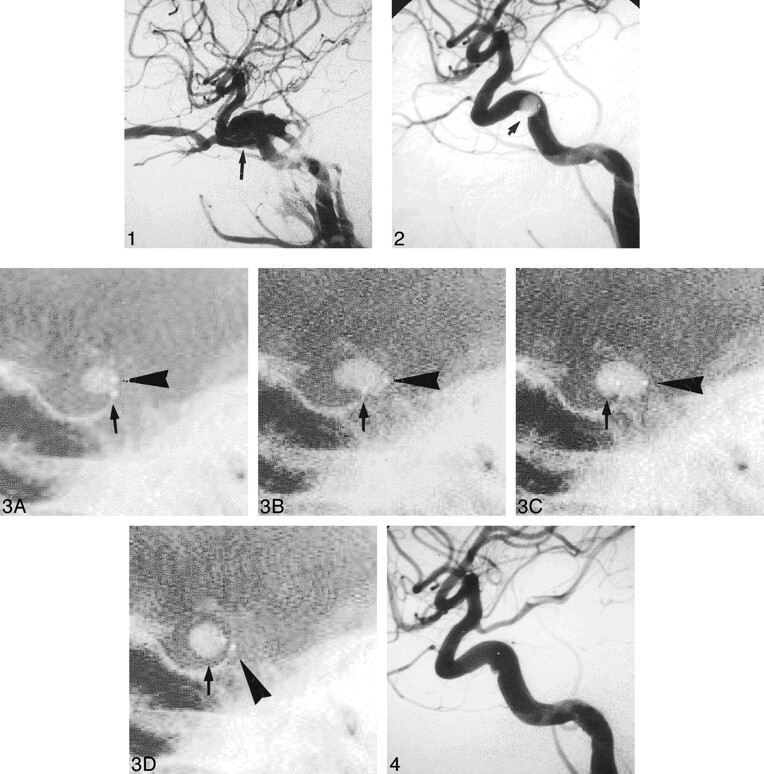
Lateral-view right carotid angiogram shows carotid cavernous fistula (arrow).fig 2. A balloon (arrow) is sucked to the fistula in the ICA. However, it cannot pass through the fistula to enter the CS. This is the first indication for using the double-balloon technique.fig 3. Steps involved in double-balloon technique. The embolization balloon marked by an arrow is to remain inside the CS after embolization. The bracing balloon, indicated by an arrowhead, is for temporary inflation inside the carotid artery, and will be removed after embolization.
A, The smaller balloon is the embolization balloon. It is at the arterial side of the fistula. The larger balloon is the bracing balloon. It is partially inflated now, and will be inflated further to cover the ICA surface of the embolization balloon.
B, The bracing balloon is inflated such that it is large enough to cover the inner surface of the ICA.
C, After deflation and then inflation of the embolization balloon, it is partially inflated and in the CS.
D, The embolization balloon inside the CS is inflated to its proper size to obliterate the fistula. Then, the bracing balloon is deflated and ready to be removed.
fig 4. Lateral-view carotid angiogram after embolization shows disappearance of fistula
