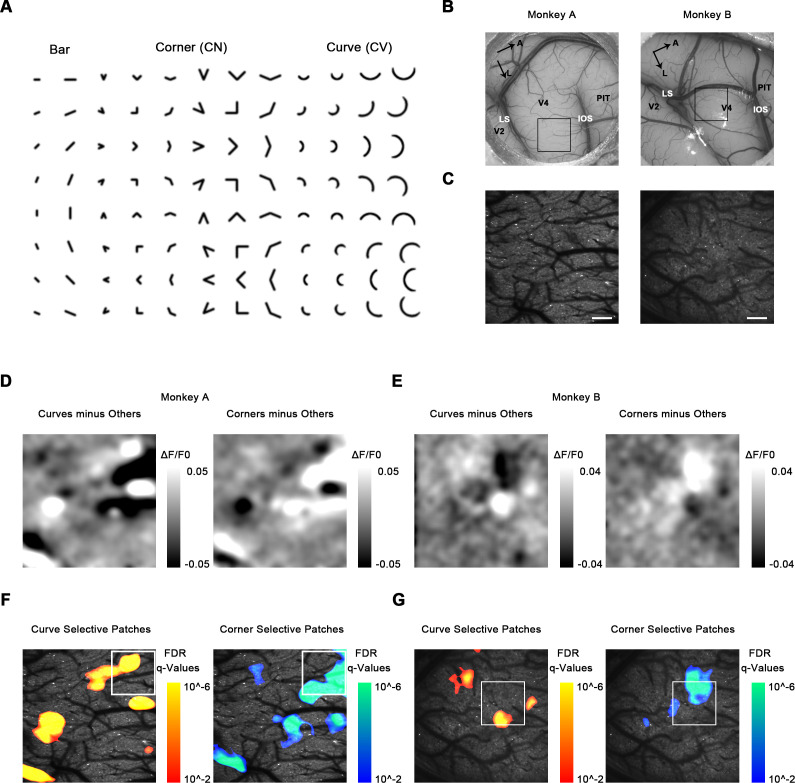
Figure 1. Cortical mapping of curve-biased and corner-biased patches in V4 using a 4× objective lens.
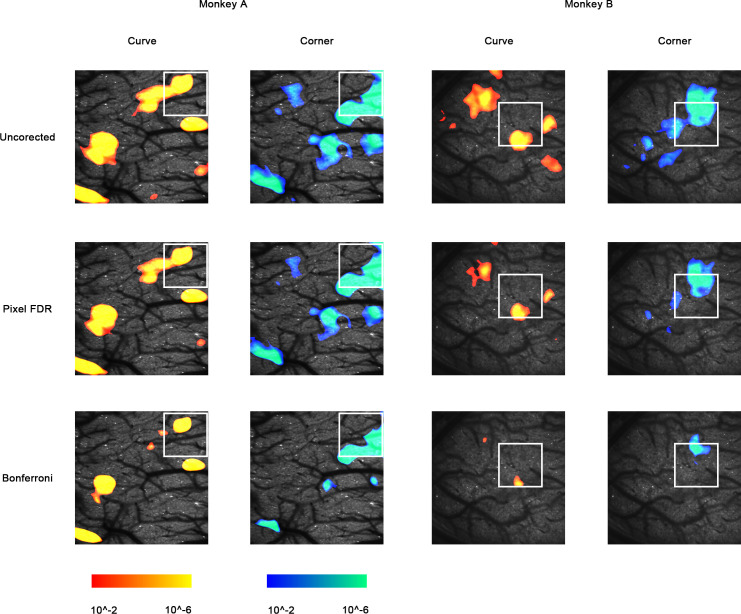
(A) The stimulus set used for initial cortical mapping consisting of bars, corners, and smooth curves. (B) Vascular map. LS: lunate sulcus; IOS: inferior occipital sulcus. The black box indicates the imaging site in each subject. (C) Two-photon fluorescence images of the two monkeys. Scale bar = 400 μm. (D) Left: subtraction map showing curve-selective activation in monkey A, derived by the average response (ΔF/F0) to all curves minus the average response to all other stimuli (corners and bars). Right: subtraction map showing corner-selective activation in monkey A. (E) The equivalent of (D) for monkey B. (F) Left: significant curve patches in monkey A. For each pixel, independent t-tests were performed to compare the responses to all curves against all corners and against all bars. Benjamini-Hochberg procedure was used to compute the pixel FDR (false discovery rate, see Materials and methods). Threshold q = 0.01. The white box indicates the imaging site selected for 16× objective single-cell mapping. Right: significant corner patches in monkey A. (G) The equivalent of (F) for monkey B.