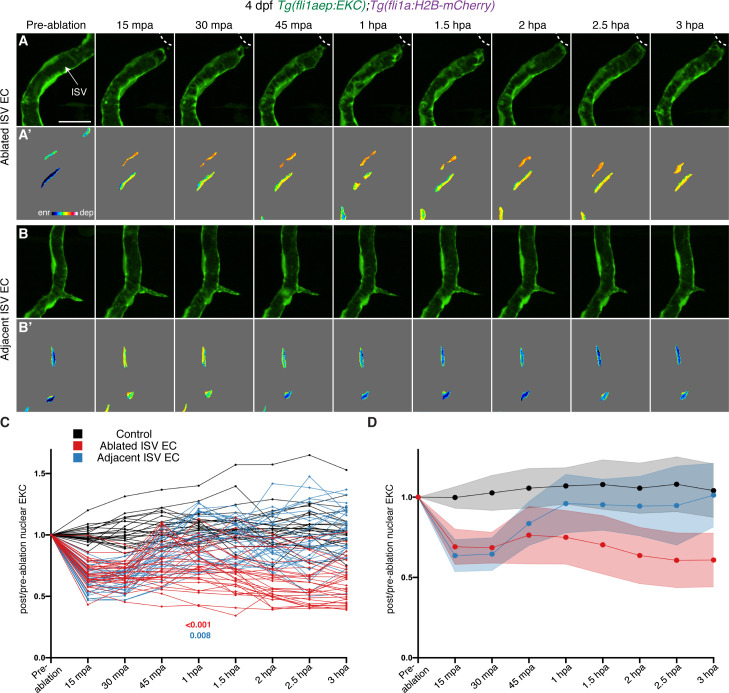
Figure 4. Wounded but not adjacent vessels maintain high Erk activity as the regenerative response proceeds.
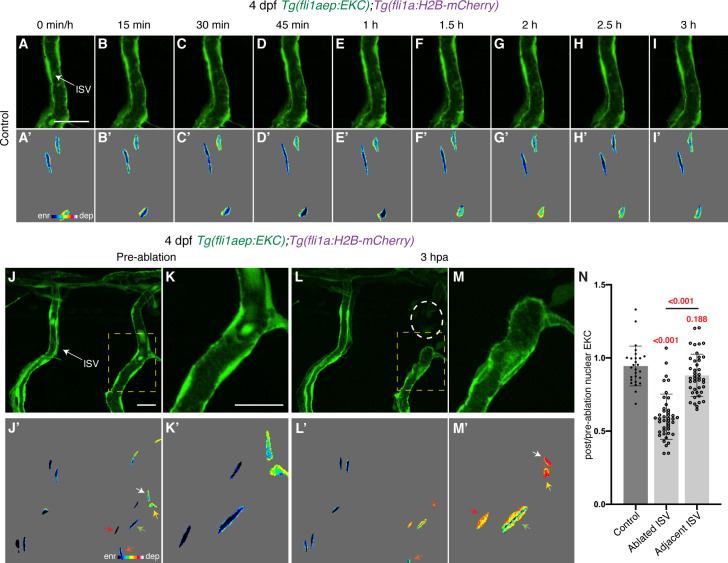
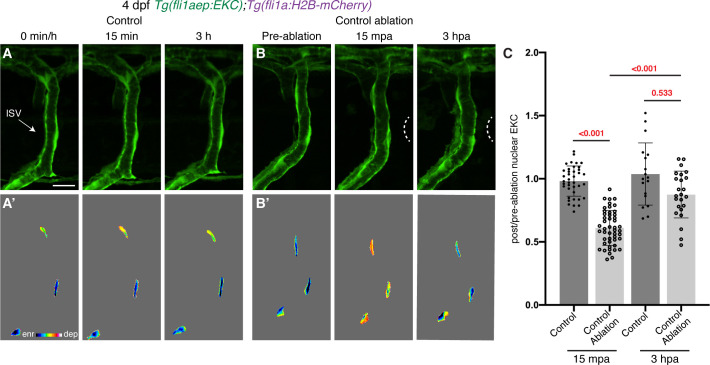
(A–B’) Lateral spinning disc confocal images of ablated (A) and adjacent ISVs (B) of a 4 days post-fertilisation (dpf) EC-EKC larva before and following vessel wounding at indicated timepoints. Erk activity is progressively lost in the adjacent but retained in the wounded ISV endothelial cells (ECs). Images (A) and (B) show fli1aep:EKC expression, and images (A’) and (B’) show nuclear fli1aep:EKC intensity. White dotted lines show the wounded site. (C,D) Quantification of post-/pre-ablation nuclear EKC intensity of ECs in non-ablated control ISVs (black, 24 ECs, n = 8 larvae), ablated ISVs (red, 30 ECs, n = 10 larvae), and adjacent ISVs (light blue, 30 ECs, n = 10 larvae) before and after vessel wounding at indicated timepoints. Graph (C) shows the quantification of individual ECs and graph (D) shows the average of all biological replicates. At 1 hour post-ablation (hpa): control vs ablated ISV ECs: p>0.001; control vs adjacent ISV ECs: p=0.108 (Kruskal-Wallis test). ISV: intersegmental vessel. Statistical test: permutation test was conducted for graph (C). Error bars represent standard deviation. Scale bar: 20 μm.