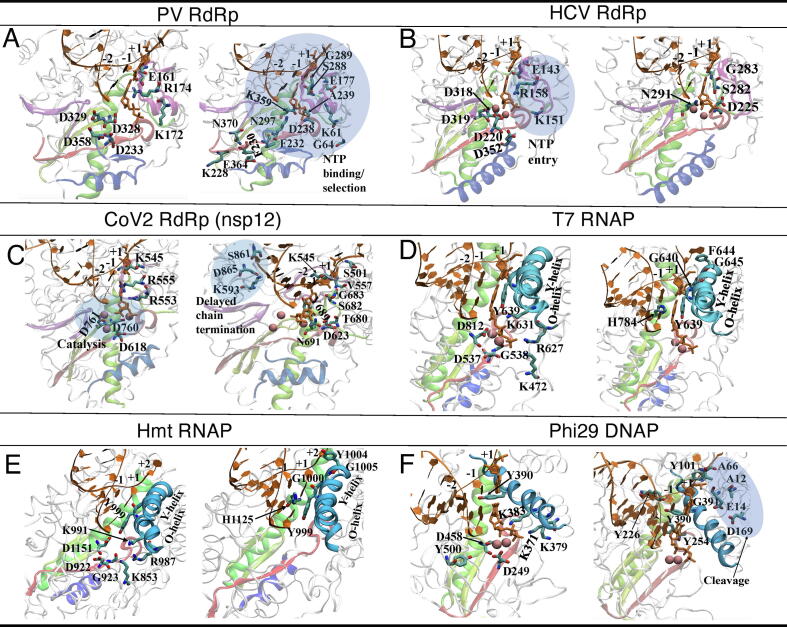
Fig. 2.
The key residues involved in NTP entry, NTP binding or selection, and catalysis in the individual viral polymerases. For clarity, the catalysis/NTP entry related residues are shown (left) separately from those involved in the NTP binding/selection (right). (A) The key residues shown for Polio virus (PV) RdRp (or 3Dpol; PDB:3OLB; the NTP binding/selection residues identified are shaded and detailed in text). (B) The key residues shown for HCV RdRp (NS5B; PDB:4WTA; the NTP entry residues identified are shaded and addressed in text). (C) The key residues shown for SARS-CoV-2 RdRp (PDB:7BTF; the conserved catalytic residues and the residues potentially involved in the delayed chain termination are shaded and addressed in text, along with the key residues to be involved in the NTP-entry, binding/selection). (D) The key residues shown for T7 RNAP, with the O-helix and Y-helix on the fingers subdomain highlighted (PDB:1S0V; the NTP binding/selection residues are addressed in the related work [10]). (E) The key residues shown for human mitochondrial (hmt) RNAP (or POLRMT), with the O-helix and Y-helix highlighted (PDB:4BOC; the residues are shown similarly as in T7 RNAP). (F) The key residues shown for phi29 DNAP, with a comparable helix from the fingers subdomain highlighted [residue 375–390 overlap with the motif B; PDB:2PYL; the proofreading/cleavage involved residues are shaded (with Asp to Ala mutations); other residues are addressed in text].