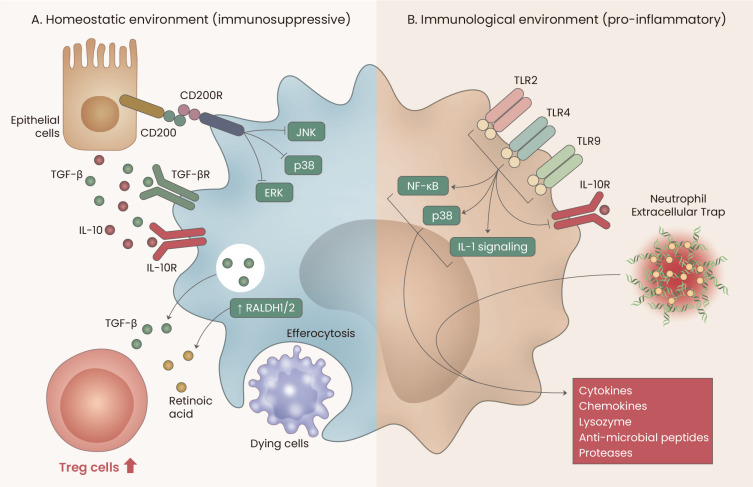
Fig. 3. Immunological functions of AMs.
(A) Under homeostatic conditions, lung epithelial cells continuously provide immunosuppressive signals to AMs by producing CD200, IL-10, and TGF-β. Subsequently, AMs contribute to regulatory T cell generation by secreting TGF-β and by expressing retinal dehydrogenases 1/2 (RALDH1/2). Moreover, AMs phagocytose dying cells to maintain the alveolar homeostatic environment. (B) Under inflammatory conditions, toll-like receptor (TLR) signals and/or neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) trigger AMs to functionally switch to pro-inflammatory roles.