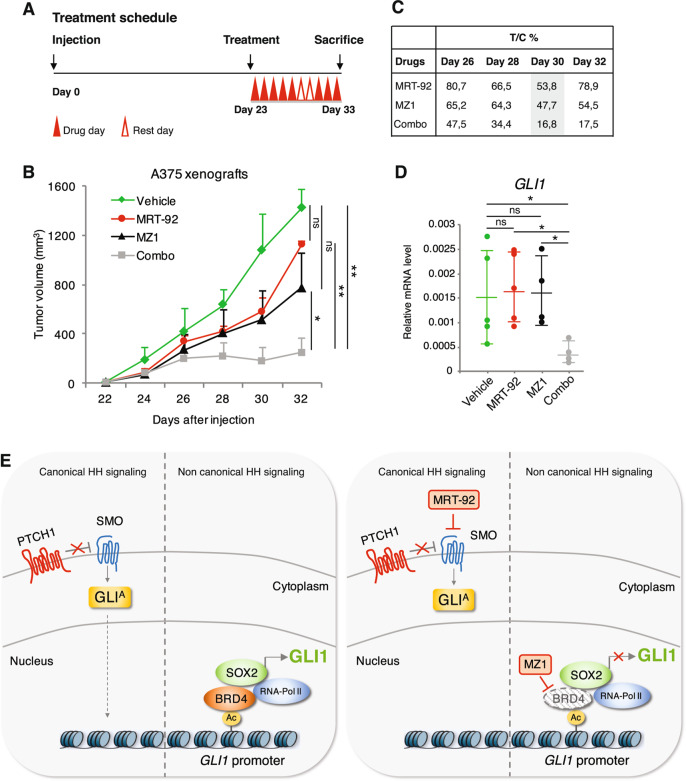
Fig. 7. Efficacy of MRT-92 and MZ1 combination in vivo.
A Schematic illustration of treatment schedule. B In vivo orthotopic tumor growth of A375 cells in athymic nude mice. At tumor appearance mice were randomized in four groups and treated i.p. with vehicle alone, MRT-92 (15 mg/Kg, BID), MZ1 (100 mg/Kg, QD), or combination (n = 7 for each group). C Table shows percentage of tumor volume reduction in treated groups compared to vehicle-treated group (% T/C ratio). D Dot plot quantification of GLI1 expression by qPCR in A375 xenografts (n = 5 for each group). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. P values were calculated by ANOVA with Tukey’s test (B) or two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test (D). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ns not significant. E Schematic representation of canonical and non-canonical HH signaling and their inhibition by MRT-92 and MZ1. Left, non-canonical activation of GLI1 in melanoma: SOX2 and BRD4 form a complex, and BRD4, by interacting with acetylated histones in the proximal region of the GLI1 promoter, induces RNA polymerase 2 activity and transcriptional activation of GLI1. Right, the SMO antagonist MRT-92 inhibits canonical HH signaling, whereas MZ1 induces BRD4 degradation with consequent inhibition of GLI1 transcription.