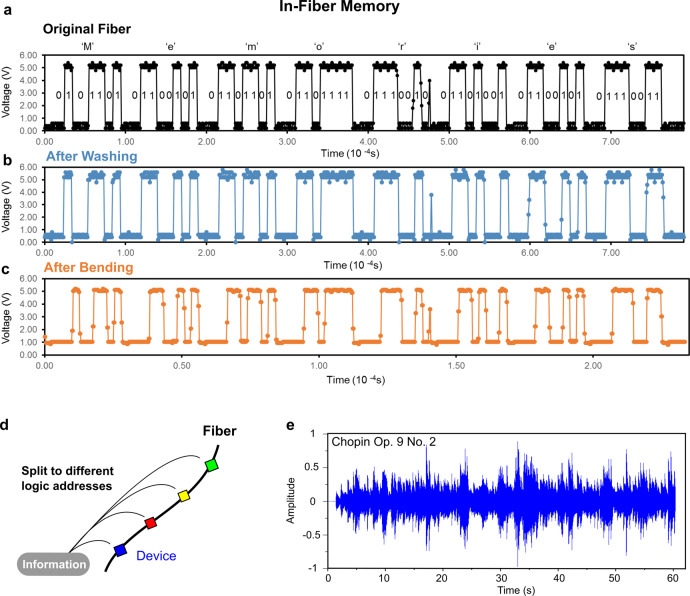
Fig. 3. Storage of information in fibres.
a Writing and reading of binary information (the word ‘Memories’), in and out of the fibre via digital signals communicated through its signal electrode, for the originally thermal drawn fibre (clock frequency:100 kHz), b reading of the fibre after washing for 10 cycles (clock frequency: 100 kHz), and c reading of the fibre after bending it with a curvature of radius of 12 mm (clock frequency: 300 kHz). d To store large information into the fibre, the information is split and stored into different memory devices along the fibre. Within 1 metre of fibre, 767 kilobits of information can be stored. e The plot of a 0.48 megabyte music piece written into the textile, stored for 2 months with no power, and later read out from the textile integrated with the memory fibres.