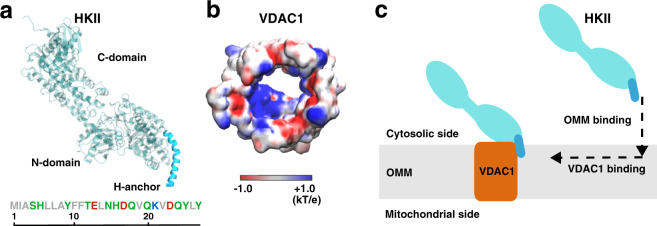
Fig. 1. HKII and VDAC1 structures and the design of our modeling approach.
a The structure of HKII contains N- and C-domains (teal), and an N-terminal helix named here as H-anchor (cyan). The amino acid sequence of H-anchor is shown below, colored by their residue types: gray representing hydrophobic, green polar, red acidic, and blue basic amino acids. b The top-down view of VDAC1 colored by its electrostatic potential, generated using the Poisson–Boltzmann (PB) equation solver in CHARMM-GUI73,86,93. c Schematic representation describing our modeling approach in which HKII binds the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) first, and then membrane-bound HKII forms a complex with VDAC1.