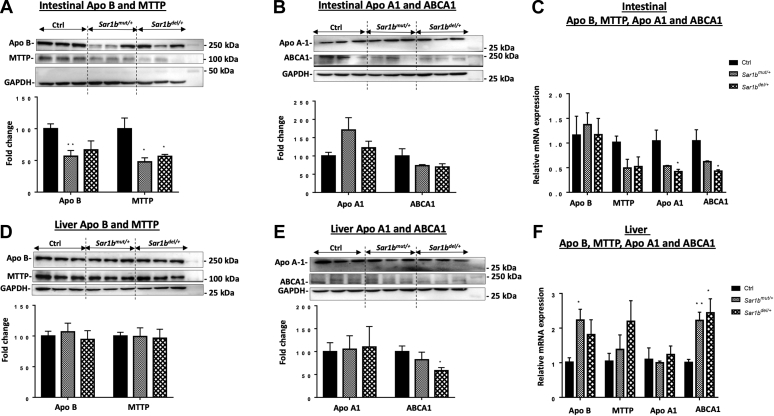
Fig. 5.
Sar1b genetic defects impair key players of intestinal chylomicron assembly and HDL biosynthesis. Wild-type, Sar1bmut/+, and Sar1bdel/+ female and male mice (9–11 weeks) were fed ad libitum with a conventional chow diet for 1 week. Prior to the sacrifice, mice were fasted 6 h and then were given 200 μl of olive oil and 4 μCi [14C]-triolein by oral gavage. Intestinal and liver tissues were collected. Protein expressions of (A, D) Apo B, MTTP, (B, E) Apo A1, and ABCA1 were analyzed by Western blot in the intestine and liver tissues, respectively. The gene expression was also assessed in (C) the intestine and (F) liver by RT-qPCR as described in the Materials and Method section. Results represent the means ± SEM of 3–6 mice in each group. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 versus wild-type mice (Ctrl).