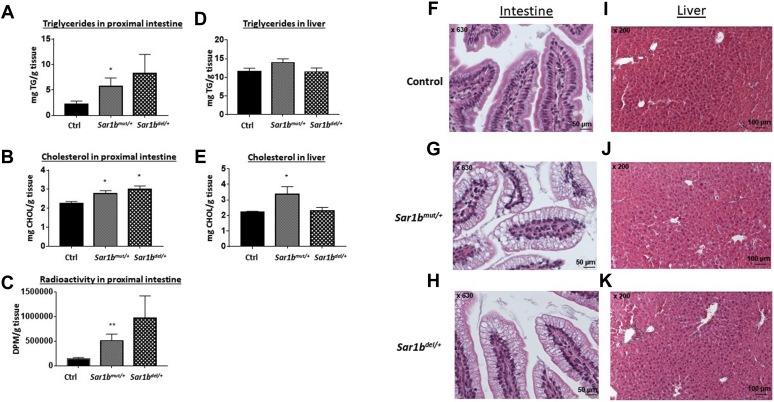
Fig. 6.
Effect of Sar1b genetic defects on intestinal and hepatic lipid accumulation. Wild-type, Sar1bmut/+, and Sar1bdel/+ female and male mice (9–11 weeks) were fed ad libitum with a conventional chow diet for 1 week. Prior to the sacrifice, mice were fasted 6 h and then were given 200 μl of olive oil and 4 μCi [14C]-triolein by oral gavage. A and D: Triglycerides and (B, E) total cholesterol were extracted from the gut and liver, and the same for (C) radioactivity derived from the labeled [C14]-triolein. They were all analyzed as described in the Materials and Method section. Finally, monographs of histology with hematoxylin-eosin were analyzed and expressed in the (F, G, H) intestine and (I, J, K) liver. Results represent the means ± SEM of 10–13 mice in each group. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 versus wild-type mice (Ctrl).