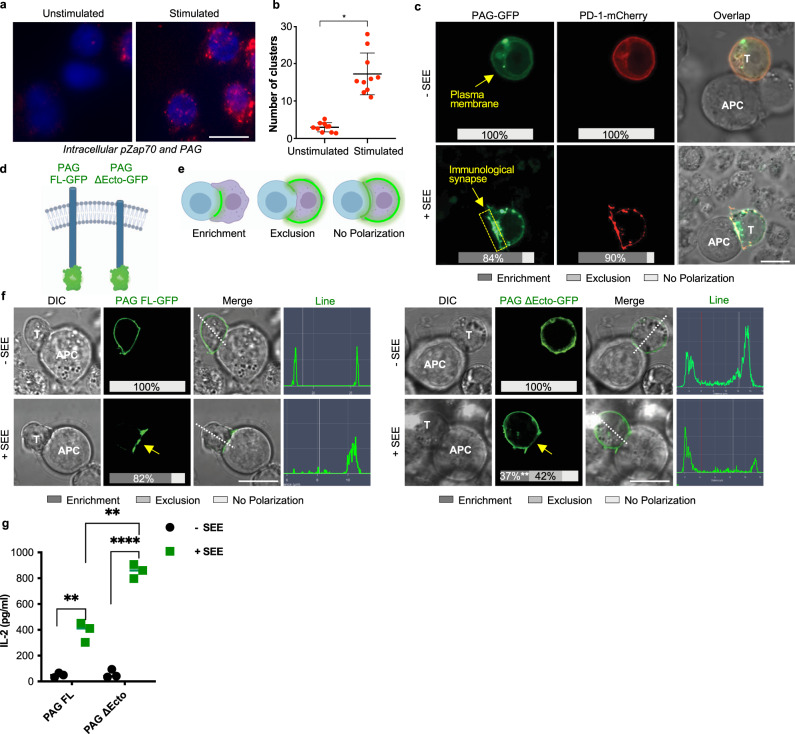
Fig. 4. PAG colocalizes with PD-1 at the immunological synapse.
a Jurkat T cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 and microcluster localization of phosphorylated Zap70 and PAG was assessed by the proximity ligation assay. b Quantification of clusters from the proximity ligation assay (a). c Jurkat cells transfected with PAG-GFP and PD-1-mCherry then incubated with Raji cells in the presence or absence of superantigen SEE. Inset percentages represent the percentage of counted cells with the represented phenotype. Fifty cells were counted for each condition in three independent experiments. d Schematic of PAG constructs—full length, wild type PAG (PAG FL); extracellular domain deletion of PAG (PAG ΔEcto). e Schematic of the characterization of GFP localization. f Jurkat cells transfected with PAG FL-GFP or PAG ΔEcto-GFP then incubated with Raji cells in the presence or absence of superantigen SEE. Fifty cells were counted for each condition in three independent experiments. Inset percentages represent the percentage of counted cells with the represented phenotype, statistical comparison of % enrichment between PAG FL and PAG ΔEcto is shown. Dotted white line and histogram show representative line analysis. g ELISA of secreted IL-2 in the supernatant of Jurkat cells transfected with PAG FL or PAG ΔEcto. Jurkat cells were co-cultured with Raji cells in the presence or absence of superantigen SEE for 24 h prior to supernatant collection. Individual data points shown with median indicated of three independent experiments; scale bars represent 10 µm. **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001.