Figure 3.
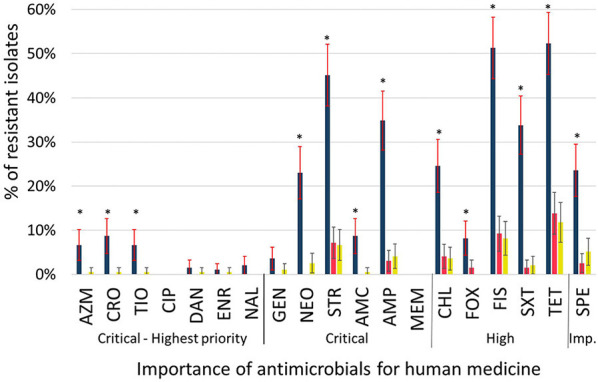
Proportion of resistant (intermediate and resistant combined) Escherichia coli isolated from calves ( ; n = 195), cows (
; n = 195), cows ( ; n = 202), and manure pits (
; n = 202), and manure pits ( ; n = 196) from 101 dairy farms from Québec, Canada. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. Importance of antimicrobial for human medicine according to World Health Organization (15). *Statistically different (p < 0.05) probabilities of resistance between isolates obtained from calves, cows, or manure pit and estimated using either a logistic regression model with robust variance to account for clustering by farm (AMP, CHL, FIS, SPT, STR, SXT, TET), or a Fisher exact test (AMC, AZM, CRO, DAN, ENR, FOX, GEN, NAL, NEO, TIO). AMC, amoxicillin-clavulanic acid; AMP, ampicillin; AZM, azithromycin; CHL, chloramphenicol; CIP, ciprofloxacin; CRO, ceftriaxone; DAN, danofloxacin; ENR, enrofloxacin; FIS, sulfisoxazole; FOX, cefoxitin; GEN, gentamicin; MEM, meropenem; NAL, nalidixic acid; NEO, neomycin; SPT, spectinomycin; STR, streptomycin; SXT, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole; TET, tetracycline; TIO, ceftiofur.
; n = 196) from 101 dairy farms from Québec, Canada. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. Importance of antimicrobial for human medicine according to World Health Organization (15). *Statistically different (p < 0.05) probabilities of resistance between isolates obtained from calves, cows, or manure pit and estimated using either a logistic regression model with robust variance to account for clustering by farm (AMP, CHL, FIS, SPT, STR, SXT, TET), or a Fisher exact test (AMC, AZM, CRO, DAN, ENR, FOX, GEN, NAL, NEO, TIO). AMC, amoxicillin-clavulanic acid; AMP, ampicillin; AZM, azithromycin; CHL, chloramphenicol; CIP, ciprofloxacin; CRO, ceftriaxone; DAN, danofloxacin; ENR, enrofloxacin; FIS, sulfisoxazole; FOX, cefoxitin; GEN, gentamicin; MEM, meropenem; NAL, nalidixic acid; NEO, neomycin; SPT, spectinomycin; STR, streptomycin; SXT, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole; TET, tetracycline; TIO, ceftiofur.
