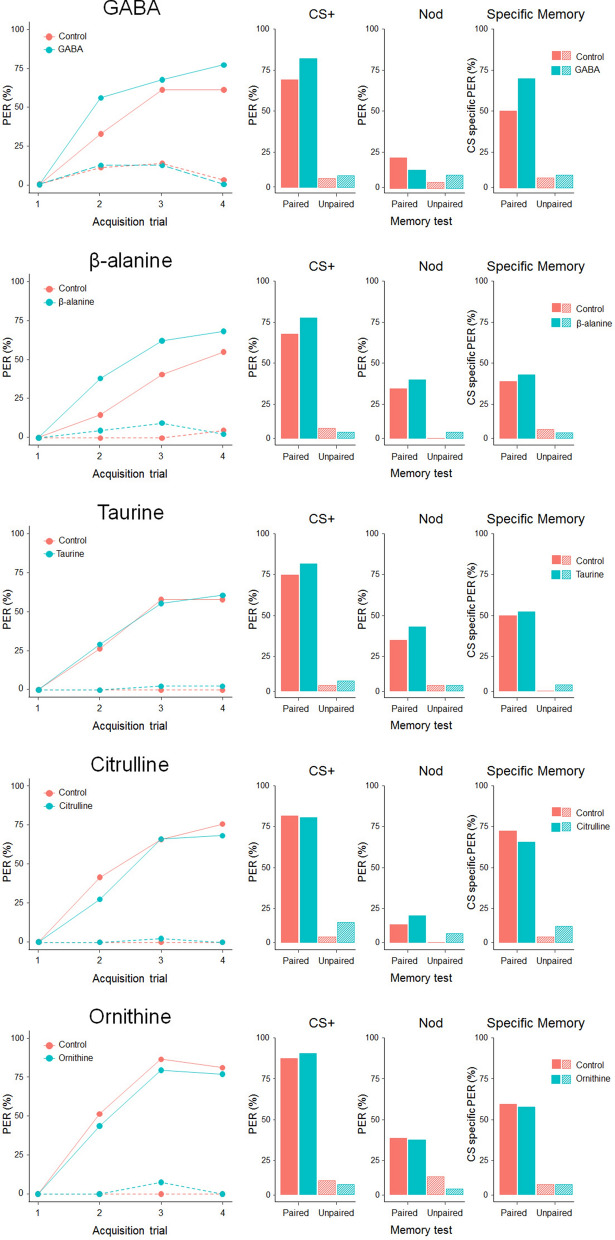
Figure 4.
Effects of NPAAs dissolved in US on appetitive olfactory learning and memory retention in harnessed bees. Acquisition trials: Percentages of PER showed by experimental (blue lines) and control (red lines) bees in the paired (solid lines) and unpaired (dotted lines) groups during the contextual conditioning experiment for each of the NPAAs. In the paired groups, GABA and β-alanine significantly enhanced the acquisition performances of bees (GLMM, GABA: p = 0.027; β-ALA: p = 0.009). None of the other NPAAs affected learning performances (all cases: p > 0.4). Unpaired groups did not learn the US-CS association (all cases: p > 0.7). Memory test: Proportions of PER showed by experimental (blue) and control (red) bees in the paired and unpaired groups during the memory test performed two hours after conditioning. GABA significantly enhanced the specific memory of bees for the trained odorant (χ2 test, p = 0.03). No difference has been found in the responses to the CS+, to the NOd or in CS−specific memory in all other cases (all cases: p > 0.1). Unpaired groups did not differ in the memory performances (all cases: p > 0.2).