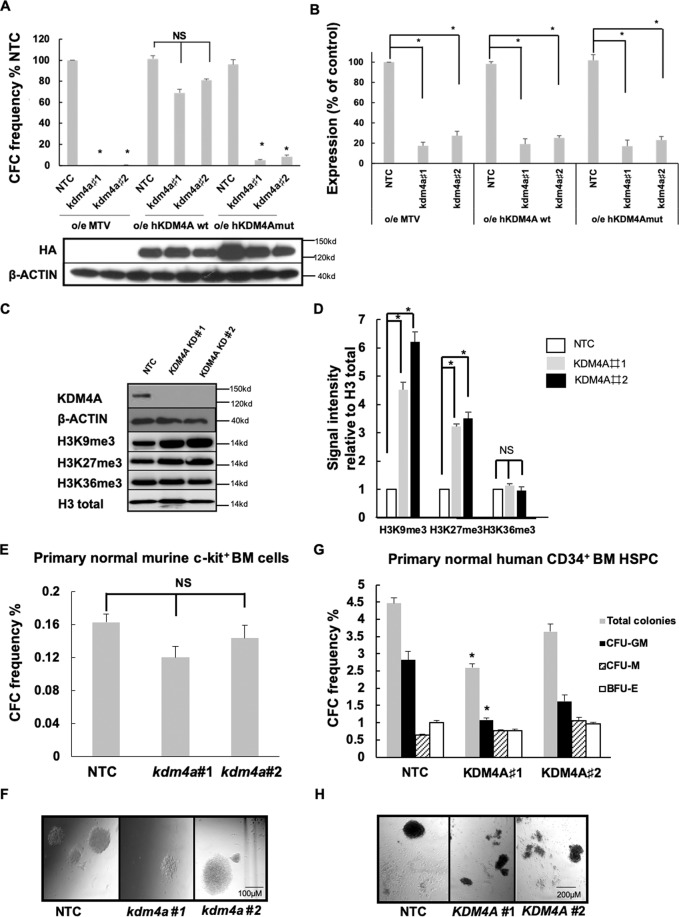
Fig. 2. Targeting KDM4A’s demethylase activity inhibits AML cell proliferation.
A CFC frequencies for control and kdm4a KD cells from the indicated murine MLL-AF9 cells overexpressing empty vector (MTV) or wild-type human HA-tagged-KDM4A or an enzymatically inactive mutant of human HA-tagged-KDM4A (KDM4Amut H188A/E190A) (n = 3); *p < 0.001, NSp > 0.05. Representative immunoblot below bar plot shows the overexpression of wild type (wt) and mutant (mut) human HA-tagged KDM4A in correlated MLL-AF9 cells labeled, detected by HA antibody. B Bar chart showing mean ± s.e.m. an expression of kdm4a by QPCR in kdm4a KD cells from (A) relative to NTC in murine MLL-AF9 leukemic cells (n = 3); *p < 0.01. C Representative immunoblots with indicated antibodies showing expression of indicated proteins in THP1 cells 72 h following initiation of KDM4A KD (n = 3). D Immunoblot quantification of signal intensity relative to H3 total from C. E–H The indicated primary human and murine AML cells were transduced with lentiviruses targeting KDM4A or kdm4a for KD, or an NTC. All bar charts show mean ± s.e.m. CFC frequencies of (E) primary normal murine c-kit+ BM cells for NTC and kdm4a KD (n = 3) or (G) primary normal human CD34+ HSPC cells for NTC and KDM4A KD cells (n = 3); *p < 0.01. F and H are representative images from (E) and (G), Scale bar represents 100 µm and 200 µm, respectively.