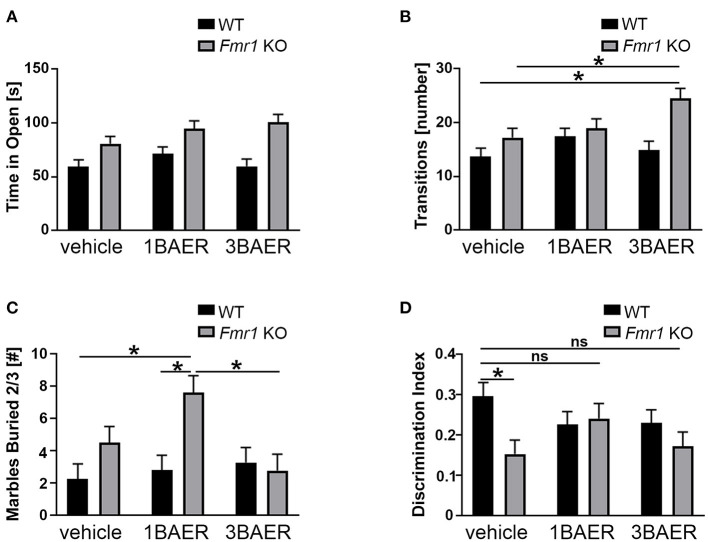
Figure 5.
BAER-101 may worsen anxiety-related and repetitive behaviors but improve memory in Fmr1 KO mice. (A,B) Fmr1 KO mice spent more time in the open (A) and made more transitions (B) than WT littermates in the elevated zero maze; BAER-101 does not affect time in the open but 3 mg/kg BAER-101 increases the number of transitions between open and closed compartments [A, 2-way ANOVA, p(genotype) < 0.0001, p(treatment) = 0.13, p(interaction) = 0.32; B, 2-way ANOVA with FDR-corrected pairwise comparisons, p(genotype) = 0.0007, p(treatment) = 0.047, p(interaction) = 0.056, *p(wt/veh-ko/3BAER) = 0.0015, *p(ko/veh-ko/3BAER) = 0.019]. (A,B) WT vehicle: n = 23, WT 1BAER: n = 25, WT 3BAER: n = 23, Fmr1 KO vehicle: n = 19, Fmr1 KO 1BAER: n = 20, Fmr1 KO 3BAER: n = 20. (C) Increased marble burying behavior in Fmr1 KO mice is enhanced by 1 mg/kg BAER-101 [2-way ANOVA with FDR-corrected pairwise comparisons, p(genotype) = 0.008, p(treatment) = 0.066, p(interaction) = 0.03, *p(wt/veh-ko/1BAER) = 0.005, *p(wt/1BAER-ko/1BAER) = 0.008, *p(ko/1BAER-ko/3BAER) = 0.008). Number of marbles buried by two thirds or more after 10 min is shown. (D) 1 mg/kg BAER-101 may improve impaired novel object recognition memory in Fmr1 KO mice [2-way ANOVA with FDR-corrected pairwise comparisons, p(genotype) = 0.028, p(treatment) = 0.62, p(interaction) = 0.073, *p(wt/veh-ko/veh) = 0.040, all other pairwise comparison not significant]. Shown is the discrimination index DI [(time with the novel object—-time with familiar object)/(time with the novel object + time with the familiar object)]. (C,D) WT vehicle: n = 23, WT 1BAER: n = 25, WT 3BAER: n = 24, Fmr1 KO vehicle: n = 21, Fmr1 KO 1BAER: n = 20, Fmr1 KO 3BAER: n = 20. *indicates a significant difference, ns indicates not significant.