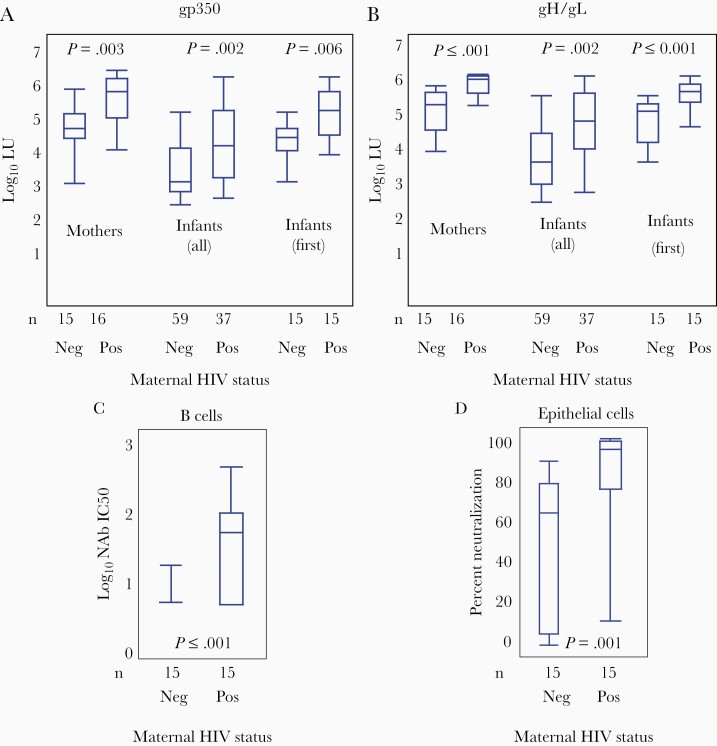
Figure 2.
Binding antibody titers against gp350 and gH/gL and neutralization levels of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection in B and epithelial cells. Distribution of log10 light units (LU) for gp350 (A) and gH/gL (B), a measure of the antibody titer, by maternal human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) status, positive (Pos) or negative (Neg). Data are shown for first maternal samples at birth, all infant samples prior to EBV infection, and first infant sample (6 weeks). Neutralizing antibody levels in B cells (C) and epithelial cells (D) in infants based on the HIV status of their mothers. Boxes represent the interquartile range, whiskers represent the minimum and maximum values, and horizontal bars show the median values. Exact 2-sample Wilcoxon test was used to compare both maternal data and data from first sample per infant by maternal serostatus. Generalized estimated equations were used to compare all infant pre-EBV infection samples against gp350 and gH/gL between HIV exposed and unexposed infants. P < .05 was considered significant.