Figure 4.
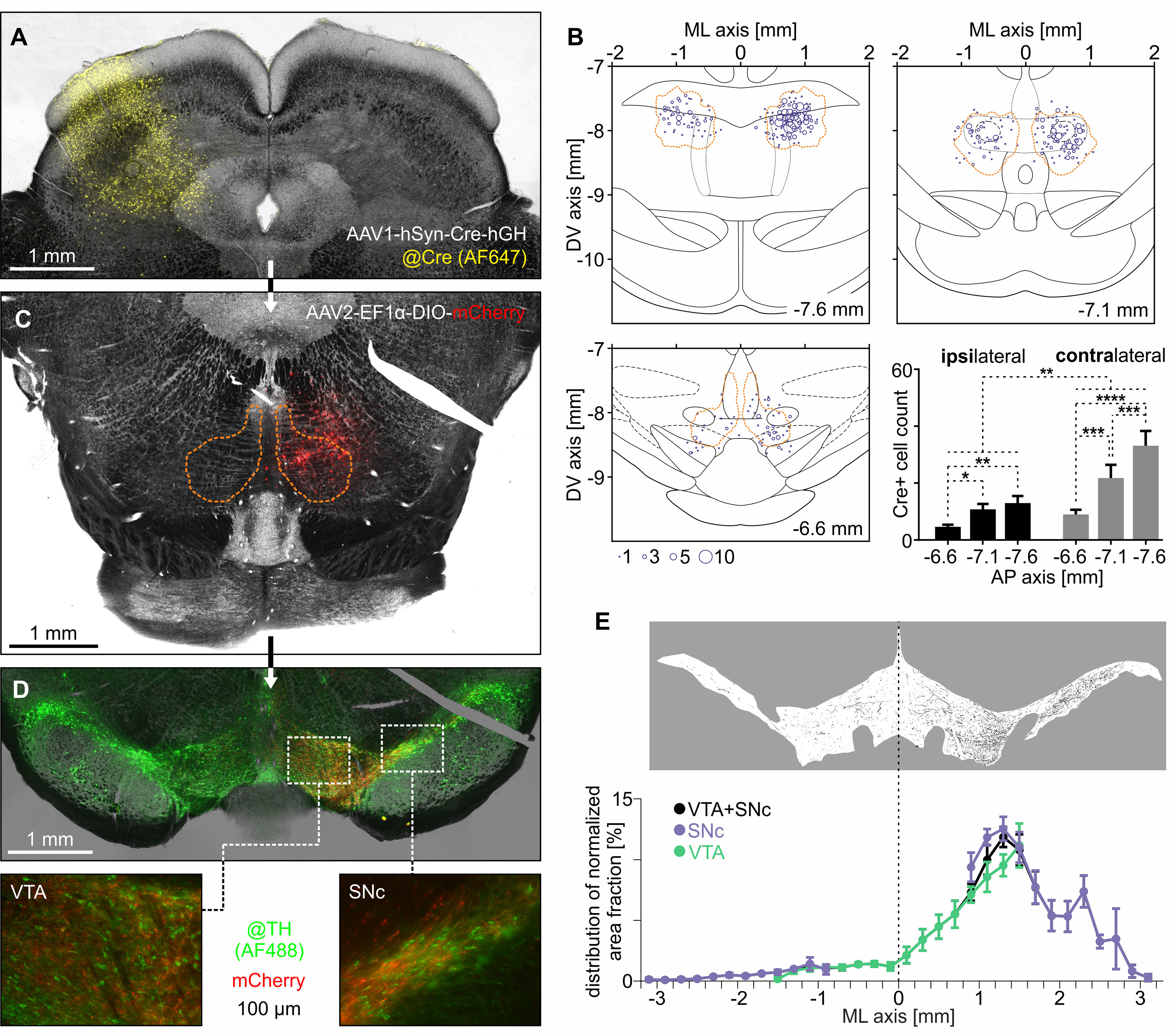
RMTg neurons monosynaptically innervated by the contralateral SC project to the midbrain dopaminergic system. A, Exemplary brain image showing the site of unilateral injection of anterograde transsynaptic AAV (AAV1-hSyn-Cre-hGH) containing the gene for Cre recombinase into the SC. Immunohistochemical staining was performed to visualize Cre-recombinase (Alexa Fluor 647; yellow color). B, Transsynaptically labeled Cre-positive neurons within RMTg. The orange dashed line indicates the RMTg boundaries based on the anti-FoxP1 immunostaining. C, Representative image of RMTg after the follow-up injection of AAV (AAV2-EF1α-DIO-mCherry) carrying Cre-dependent gene for fluorescent protein (mCherry; red color). The orange dashed line indicates the RMTg boundaries based on the anti-FoxP1 immunostaining. D, Top, Representative image of VTA and SNc after the injections of anterograde transsynaptic AAV (containing Cre recombinase gene) into the SC and AAV with Cre-dependent gene for mCherry into the contralateral (right in this case) RMTg. Immunohistochemical staining was performed to visualize TH-positive neurons (Alexa Fluor 488; green color). Bottom panels, Magnified regions of VTA and SNc with mCherry-expressing axons originating in the RMTg neurons innervated by the contralateral SC. E, Top, Exemplary image of binarized mCherry-positive axons within the VTA and SNc used for area fraction calculation. Bottom, Mediolateral distribution of normalized area fraction of mCherry-expressing axons originating from the RMTg neurons innervated by the contralateral SC. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
