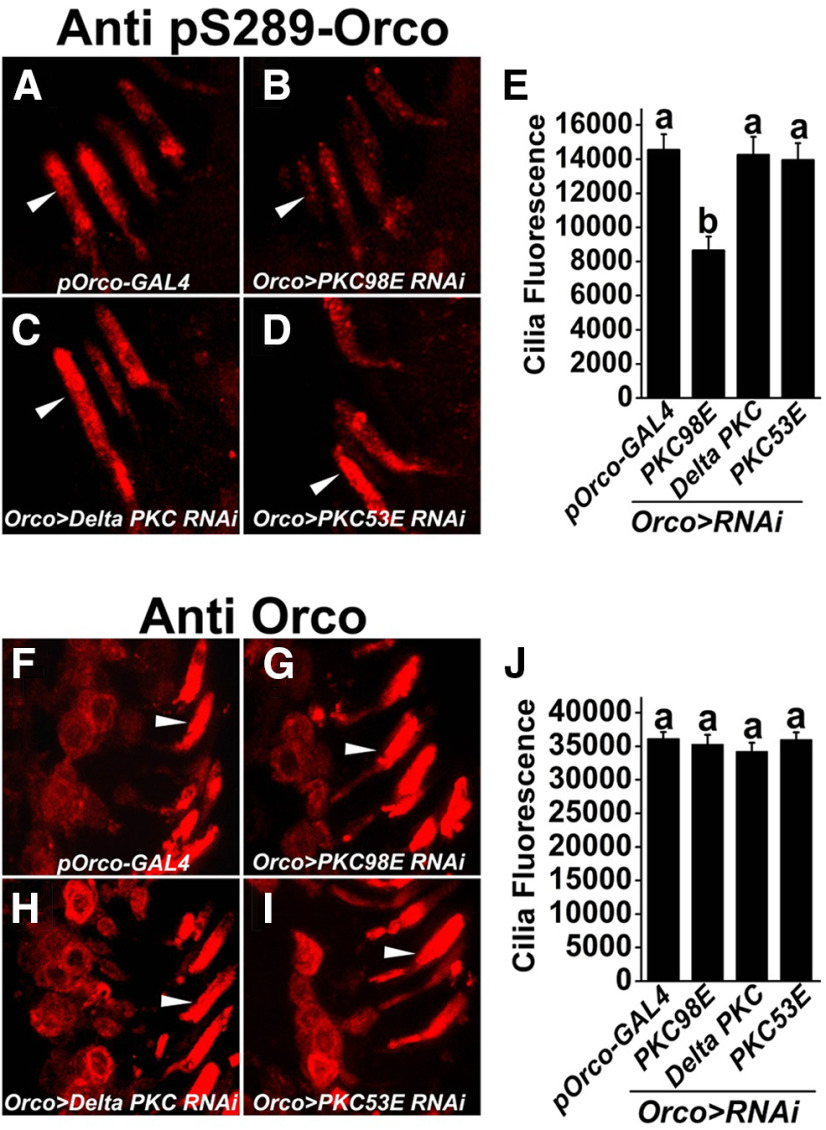
Figure 2.
PKC98E is required for normal phosphorylation of ORCO at S289 in vivo. A–D, Representative images showing the phosphorylation of ORCO at S289 in the (A) pORCO-GAL4 control, (B) PKC98E knock-down, (C) δ PKC knock-down, and (D) PKC53E knock-down (all expressed with pORCO-GAL4). Arrowheads indicate olfactory neuron dendrites. E, The phosphorylation of ORCOS289 is significantly reduced in PKC98E knock-down (b over error bar; p = 1.66 × 10−7 for PKC98E RNAi compared with pORCO-GAL4 control). There is no significant difference between pORCO-GAL4 and δ PKC RNAi (a over error bar; p = 0.90) or PKC53E RNAi, p = 0.99. PKC98E RNAi is different from δ PKC RNAi (p = 4.22 × 10−6) and PKC53E (p = 3.11 × 10−7), but there is no difference between PKC53E RNAi and δ PKC RNAi (p = 0.96). Analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey's HSD test. F–I, Representative images showing total ORCO localization in the (F) control, (G) PKC98E RNAi, (H) δ PKC RNAi, and (I) PKC53E RNAi. Arrowheads denote representative olfactory neuron dendrites. J, The quantification shows the overall localization of ORCO in the olfactory neuron dendrites is unaffected in the kinase RNAi lines. Analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey's HSD test (p = 0.94 for PKC98E RNAi vs pORCO-GAL4; p = 0.36 for δ PKC RNAi vs pORCO-GAL4; p = 0.82 for PKC53E RNAi vs pORCO-GAL4; p = 0.71 for PKC98E RNAi vs δ PKC RNAi; p = 0.82 for PKC98E RNAi vs PKC53E RNAi; and p = 0.99 for PKC53E RNAi vs δ PKC RNAi (n = 15 for each genotype). Data are plotted as mean ± SEM.