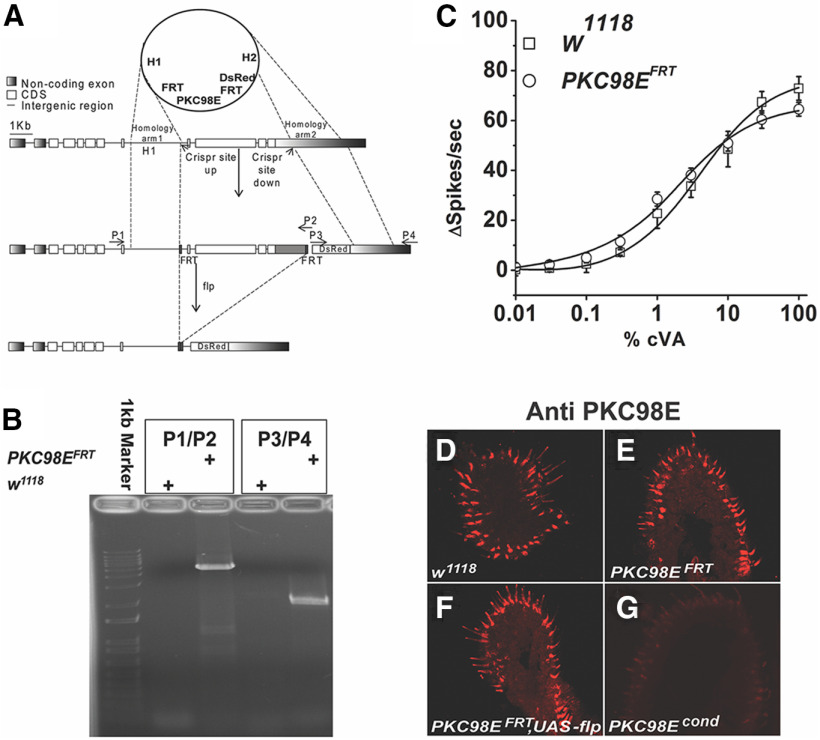
Figure 4.
Generation of PKC98E conditional null mutant. A, CRISPR/Cas9 was used to engineer FRT sites upstream and downstream of the DNA encoding the kinase domain of PKC98E (see Materials and Methods). Flies homozygous for the PKC98E FRT allele are viable and healthy. Loss of function for PKC98E in olfactory neurons was produced by introducing a transgene encoding the FLP recombinase expressed under control of the ORCO promoter. H1, homology arm 1; H2, homology arm 2; dsRed, RFP reporter gene; FRT, FLP recombination sites; P1–P4 represent PCR primer binding sites. B, PCR to validate the correct integration of the FRT allele using P1–P4 primers. C, Dose–response curve to cVA shows the FRT insertions do not alter cVA odor sensitivity in the PKC98E FRT flies in absence of the FLP recombinase (n = 5). The sigmoidal curve for Δspikes with Hill fitting was plotted for different concentrations of cVA for the w1118 and PKC98E FRT flies (p = 0.75, 0.59, 0.52, 0.25, 0.33, 0.39, 0.39, 0.73, 0.25, and 0.13 for 0.01%, 0.03%, 0.1%, 0.3%, 1%, 3%, 10%, and 100% cVA. D–G, PKC98E immunoreactivity in the conditional allele. D, w1118. E, PKC98E FRT. F, PKC98E FRT, UAS-FLP. G, PKC98E FRT conditional (pORCO-GAL4; PKC98E FRT, UAS-FLP).