Figure 6.
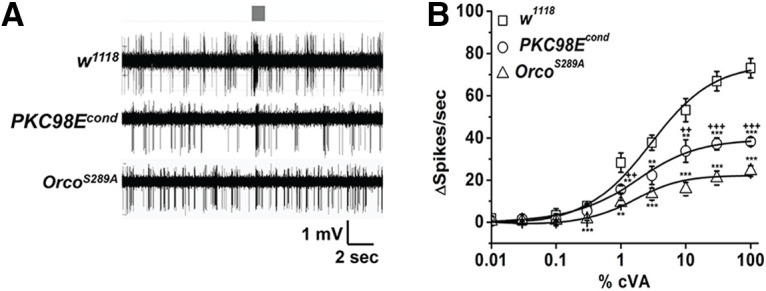
PKC98E FRT conditional mutant has reduced responsiveness to cVA. A, Sample trace for Or67d neurons from w1118, PKC98E FRT conditional mutants (pORCO-GAL4; PKC98E FRT, UAS-FLP), and ORCOS289A flies (pORCO-GAL4/UAS-OrcoS289A;orco2) to 1% cVA. Stimulus duration (300 ms) is indicated by the gray bar. B, Dose–response curve for cVA odor sensitivity for w1118 and PKC98E FRT conditional mutant and ORCOS289A (n ≥ 5). The sigmoidal curve for Δ spikes was plotted for different concentration of cVA with Hill fitting for the genotypes described. Error bars represent SEMs. One-way ANOVA analysis with post hoc Tukey's HSD test was done between control (w1118), PKC98E FRT conditional, and OrcoS289A flies; **p < 0.05, ***p < 0.01 (p values between PKC98E FRT conditional mutant and w1118 control flies are p = 0.3121, 0.83 454, 0.65152, 0.52124, 0.041, 0.032, 0.044, 0.0015, and 4.36 × 10−4 for 0.01%, 0.03%, 0.1%, 0.3%, 1%, 3%, 10%, 30%, and 100% cVA, respectively; p values comparing ORCOS289A flies and w1118 are 0.21764, 0.97444, 0.42962, 0.00189, 0.00272, 0.00109, 4.42 × 10−4, 7.05 × 10−5, and 2.39 × 10−5 for 0.01%, 0.03%, 0.1%, 0.3%, 1%, 3%, 10%, 30%, and 100% cVA, respectively. The ANOVA comparison was also done between PKC98E FRT conditional and ORCOS289A; ++p < 0.05, +++p < 0.01 (p values are 0.86982, 0.79244, 0.88431, 0.20003, 0.0144, 0.12009, 0.01867, 0.00879, and 0.00427 for 0.01%, 0.03%, 0.1%, 0.3%, 1%, 3%, 10%, 30%, and 100% cVA, respectively.
