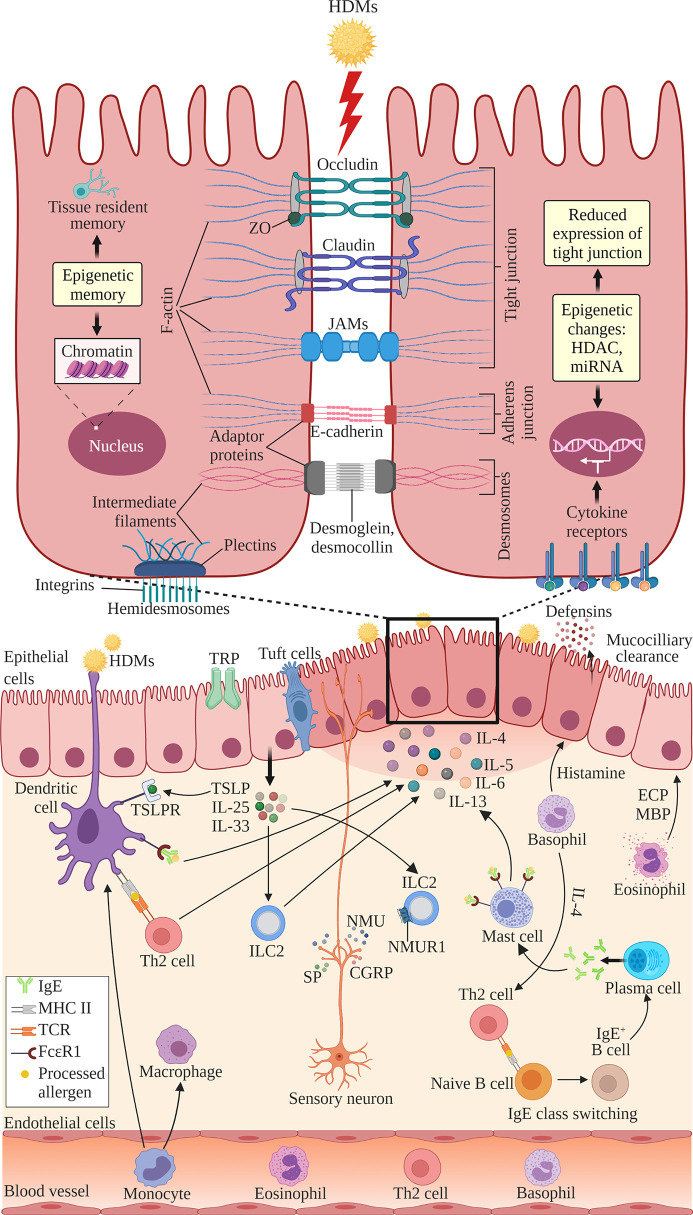
Figure 1.
The structure of nasal epithelial barrier comprises of tight junction (TJ), adherens junction, desmosomes and hemidesmosomes. TJs are composed of occludin, claudin and JAMs that span the intercellular space and intracellular adaptor proteins ZO. Adherens junctions are composed of E-cadherins and adaptor proteins. Desmosomes consist of desmoglein and desmocollin proteins that bind internal adaptor proteins. F-actin and intermediate filaments act as cytoskeleton for these cell junctions. Hemidesmosomes comprise of plectins that link to the intermediate filaments and integrins, the transmembrane linkers of extracellular matrix and actin cytoskeleton. Epithelial cells secrete antimicrobial substances such as defensins and conduct mucociliary clearance. Epithelial activation by airborne allergens during allergic response in AR leads to the activation of epithelial cells and release of epithelial-derived cytokines TSLP, IL-25 and IL-33. This triggers subsequent activation of ILC2s and production of Th2 cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, IL-6 and IL-13. Released cytokines promote DCs where they present antigens and activate naïve B cells to induce IgE class switching and maturation into plasma cells, which produce IgE. Secreted IgE binds the FcϵRI receptor on submucosal mast cells, leading to the release of preformed mediators such as histamine and inflammatory cytokines. In the late allergic phase, recruited eosinophils and basophils release mediators that further contribute to AR symptoms via epithelial damage and microvascular leaking. Blood-derived monocytes differentiate into DCs and macrophages that promote allergic responses. The overproduction of Th2 cytokines by a variety of cells suppresses the transcription of TJ molecules causing the breakdown in the nasal epithelial barrier of AR patients. Sensory neuron release NMU, SP and CGRP upon activation at sensory nerve endings. NMUR1 expressed on ILC2 intensifies the inflammatory response in the presence of IL‐25, IL‐33, and TSLP. TRP and tuft cells also have roles in regulating epithelial barrier. Epithelial barrier is also regulated by epigenetic changes through histone modification by HDACs and miRNAs. Epithelial cells exhibit epigenetic memory by embedding the memory of previous encounters within their chromatin, and tissue-resident memory cells preserve the epithelial barrier. DC, dendritic cell; ECP, eosinophil cationic protein; MBP, major basic protein; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; IgE, immunoglobulin E; ILC2, type 2 innate lymphoid cell; JAMs, junctional adhesion molecules; TCR, T cell receptor; Th2, T helper 2; TSLP, thymic stromal lymphopoietin; TSLPR, thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor; ZO, zonula occludens; HDAC, histone deacetylases; miR, microRNA; NMU, neuromedin U; NMUR1, neuromedin U receptor 1; SP, substance P; CGRP, calcitonin gene-related peptide; TRP, transient receptor potential. Created with BioRender.com.