Figure 4.
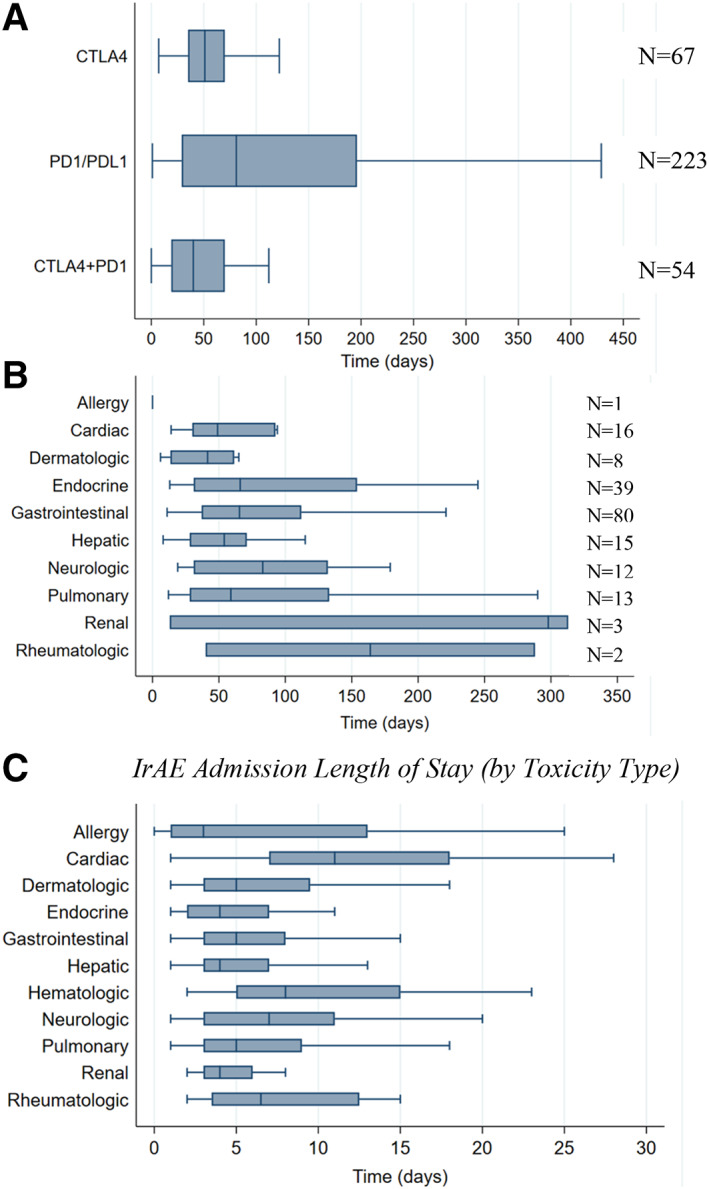
Time to first admission and length of stay of irAE admissions. (A): Time to first irAE admission was lower among CTLA‐4 monotherapy (median, 51; IQR, 35–70; p = .019) and CTLA‐4 plus PD‐1 combination therapy recipients (median, 40; IQR, 19–70; P < .001) compared with PD‐1/PD‐L1 monotherapy recipients (median, 81; IQR, 29–196). (B): Although not statistically significantly different, time to admission varied by type of confirmed irAE. (C): Length of stay per irAE admission varied significantly by toxicity type, with cardiac (median, 11; IQR, 7–18; p < .001) and neurologic irAEs (median, 7; IQR, 3–11; p = .027) associated with statistically significant increases in length of stay on multivariable linear regression. Box plots do not display outlier observations.
Abbreviations: CTLA‐4, cytotoxic T‐lymphocyte antigen‐4; ICI, immune checkpoint inhibitor; IQR, interquartile range; irAE, immune‐related adverse event.A. Time from ICI initiation to first irAE admission (by ICI and confirmed toxicity type) B. IrAE admission length of stay (by toxicity type)
