Figure 4.
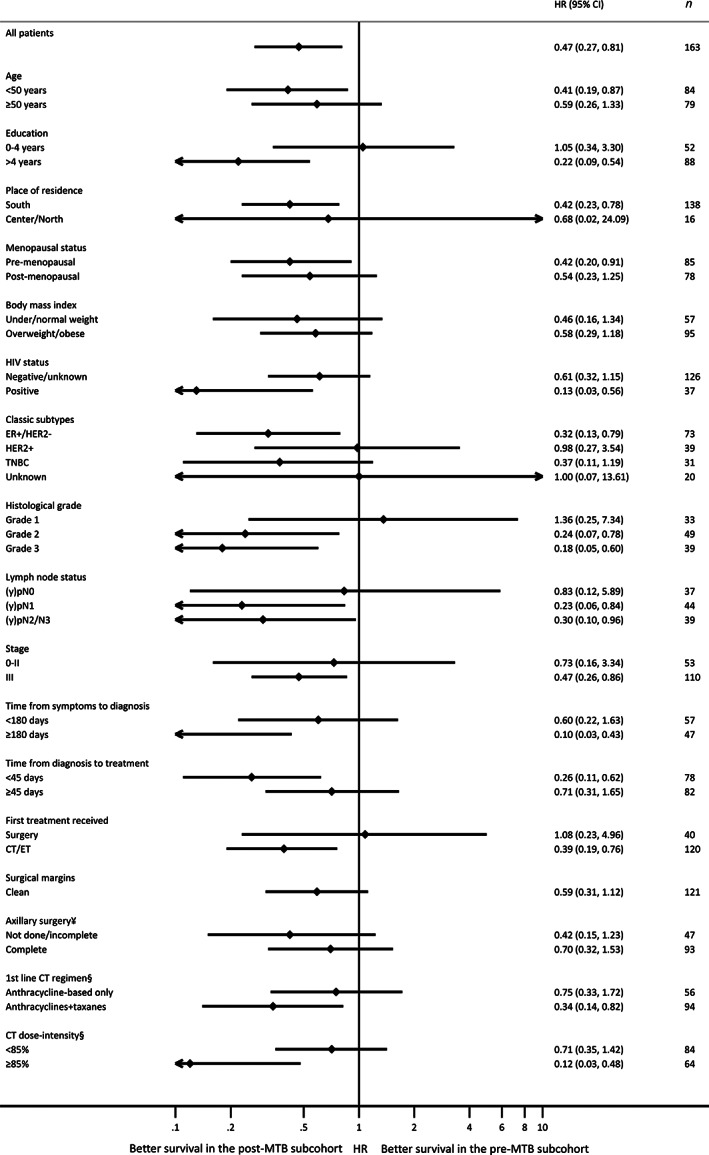
Multivariable analysis of overall survival in the post‐MTB versus pre‐MTB implementation periods within each subgroup of patients with early breast cancer (stage 0–III). All models included the following variables: MTB implementation period (pre vs. post), age (<40 vs. 40–49 vs. 50–59 vs. ≥60 years), HIV status (negative/unknown vs. positive), stage at diagnosis (0–II vs. III), and tumor subtype (ER+/HER2− vs. HER2+ vs. TNBC vs. unknown). ¥Among patients receiving any type of breast surgery. Not done/incomplete: 0–5 isolated lymph nodes (in case of axillary lymph node dissection); complete: ≥6 isolated lymph nodes (in case of axillary lymph node dissection) or ≥ 1 isolated lymph nodes with ≤2 positive lymph nodes (in case of sentinel lymph node biopsy). §First‐line of chemotherapy that the patient received includes neoadjuvant and/or adjuvant treatment. If the patient received part of chemotherapy as neoadjuvant (e.g., doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide [AC] regimen) and another part as adjuvant chemotherapy (e.g., paclitaxel), the type of regimen and dose‐intensity refer to the entire scheme (neoadjuvant plus adjuvant). Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; CT, chemotherapy; ER, estrogen receptor; ET, endocrine therapy; HR, hazard ratio; MTB, multidisciplinary tumor board; TNBC, triple‐negative breast cancer.
