Figure 8.
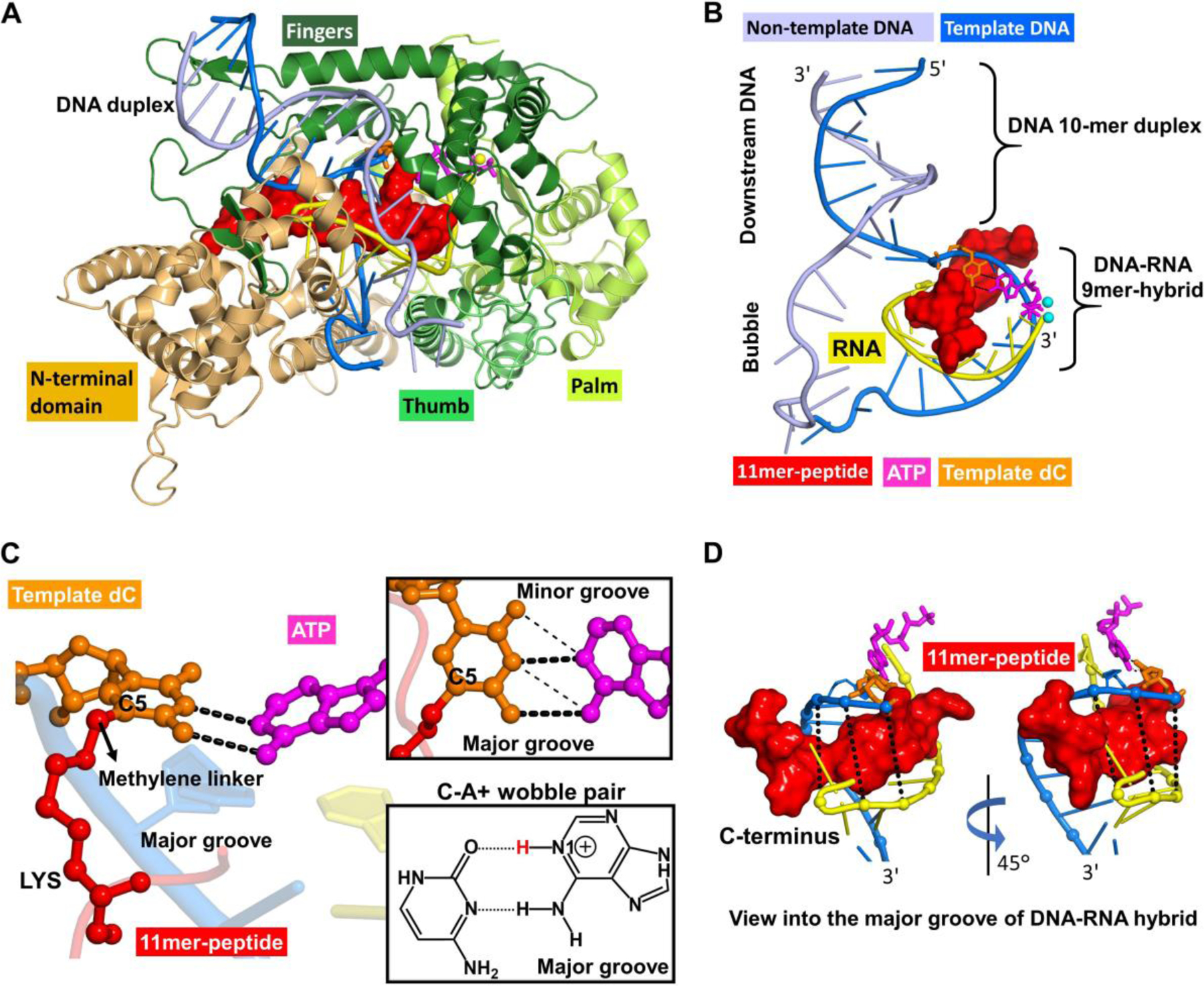
Overall structure of the T7 RNA polymerase complex in the insertion state, showing the 11mer-peptide cross-linked to the templating dC opposite incoming ATP to form a C-A+ mismatch pair. (A) This complex includes protein domains and nucleic acids in cartoon rendering. The enzyme domains consist of the N-terminus (residues 1−325), thumb (residues 326−411), palm (residues 412−553 and 785–883), and fingers (residues 554−784). (B) A view without enzyme. The nucleic acids include template and non-template DNA, RNA and an incoming ATP. The DNA consists of a part with a 10-mer duplex in the downstream region and a noncomplementary segment in the open bubble. A complementary nine nucleotide RNA segment at the 3'-end is hybridized to the template DNA in the bubble region to form the DNA-RNA hybrid 9-mer. (C) A view of the active site from the major groove showing the templating dC paired with incoming ATP via two hydrogen bonds. (inset box, thick dashed lines), which shifted from the standard wobble pairing scheme (thin dashed lines) in our MD simulations. The chemical structure of the C-A+ wobble pair, containing two hydrogen bonds, dC(N3) − A+(N6H2) and dC(O2) − A+(N1H) with glycosidic bonds anti in both dC and A+, is also displayed. The C5 atom of templating dC is conjugated to the side chain of a lysine residue in the 11mer-peptide via a methylene linker. (D) Views of the DNA-RNA hybrid structure highlighting the 11mer-peptide tightly-held in the narrow major groove of the hybrid. The C-terminus of the 11mer-peptide is directed toward the 3'-end of the DNA template strand.
