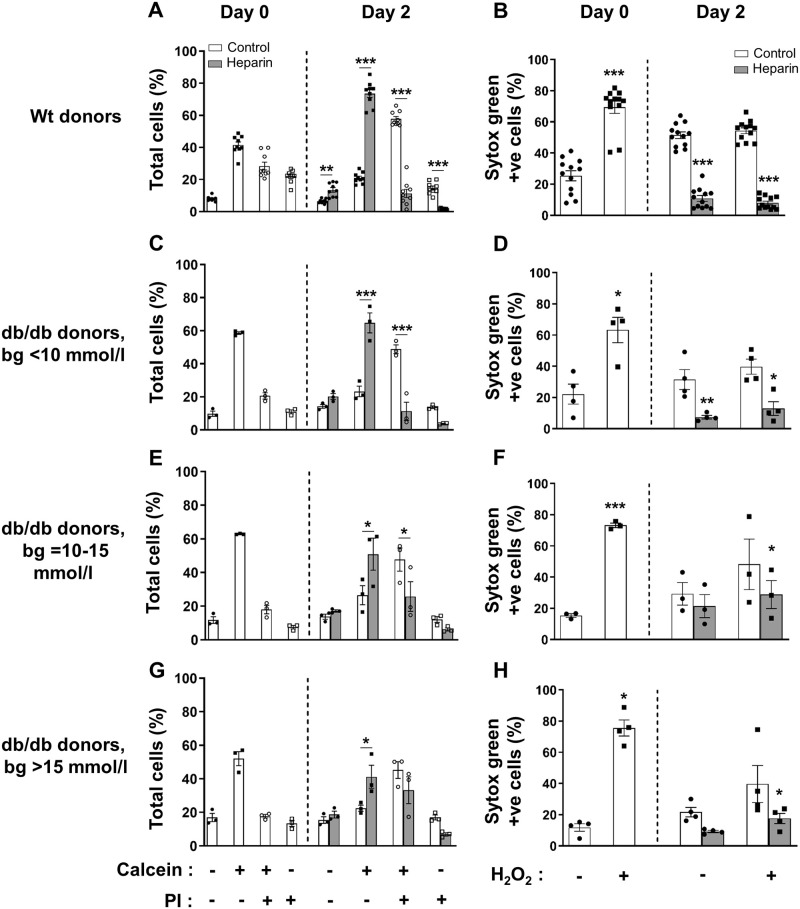
Fig 7. HS replacement protects db/db beta cells from dying in culture and from acute hydrogen peroxide-induced damage.
The viability of (A) wt and (C, E, G) db/db beta cells was analyzed by flow cytometry using the fluorescent dyes Calcein (Cal) and PI after culture for 2 days without (open bars) or with (shaded bars) the highly sulfated HS analogue heparin (50 μg/ml). Cell death/damage due to acute treatment with hydrogen peroxide was measured by uptake of the fluorescent dye Sytox Green. Donors were (A, B) wt; (C, D) normoglycemic db/db (bg<10 mmol/l); (E, F) mildly hyperglycemic db/db (bg = 10–15 mmol/l) and (G, H) severely hyperglycemic db/db (bg>15 mmol/l). Beta cells were identified as viable (Cal+PI-), damaged (Cal+PI+) or dead (Cal-PI+) and expressed as % total cells; alternatively, damaged/dead cells were identified as Sytox Green+ve. Data represent mean ± SEM for n = 3–11 experiments/group; n = 2–4 male donors/experiment. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 and ***p<0.0001, ANOVA with Fisher’s unprotected LSD post-test.