Figure 2.
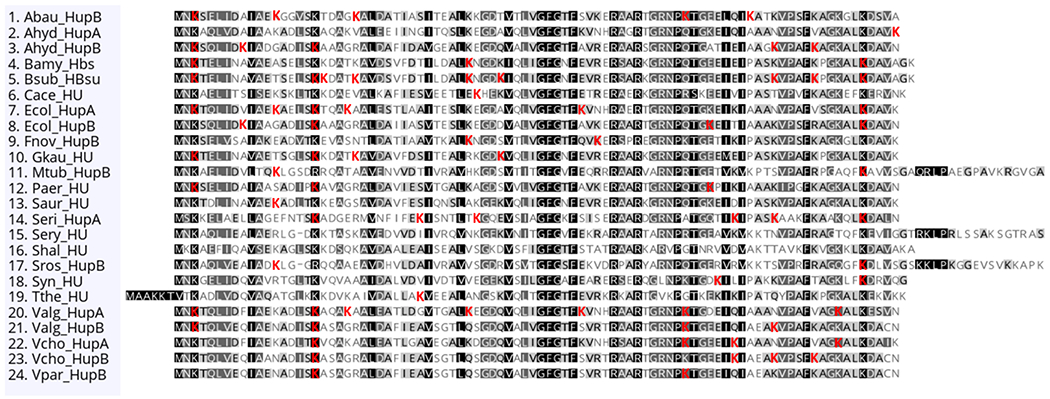
Evolutionary conservation of lysine acetylation of HU orthologues. HU orthologous sequences were obtained from the NCBI protein database. For some bacterial species, the HU orthologues exist as heterodimers, and the two subunits are denoted as HupA and HupB. The sequence alignment was performed using Geneious Prime, version 2020.1.1; the level of shading indicates the level of conservation, with black the best conserved. The identified acetylation sites from the acetylome studies listed in Table 1 are highlighted in red. The Actinobacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Saccharopolyspora erythraea, and Streptomyces roseosporus) contain a unique C-terminal extension that is rich in basic amino acids. The entire extension is about 110 amino acids and is not shown. Species included: Acinetobacter baumannii (Abau), Aeromonas hydrophila (Ahyd), Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (Bamy), Bacillus subtilis (Bsub), Clostridium acetobutylicum (Cace), Escherichia coli (Ecol), Francisella novicida (Fnov), Geobacillus kaustophilus (Gkau), M. tuberculosis (Mtub), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Paer), Staphylococcus aureus (Saur), Spiroplasma eriocheiris (Seri), S. erythraea (Sery), Sulfurospirillum halorespirans (Shal), S. roseosporus (Sros), Synechococcus sp. (Syn), Thermus thermophilus (Tthe), Vibrio alginolyticus (Valg), Vibrio cholerae (Vcho), and Vibrio parahemolyticus (Vpar).
