Fig. 4. Loss of Kismet in SPG leads to fragmented sleep in the larval stage.
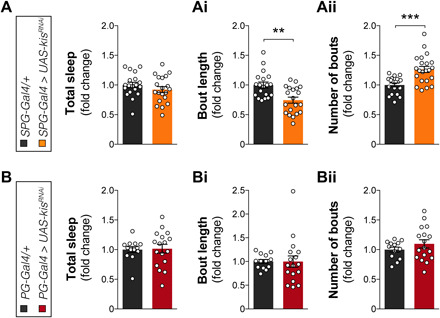
Kismet knockdown in SPG with the R54C07-Gal4 driver (SPG-Gal4 > UAS-kisRNAi-2, in orange, n = 20) compared to background controls (SPG-Gal4/+, in black, n = 19) does not alter the (A) total amount of larval (second instar) sleep (quiescence bouts) (P = 0.7, t = 1.149, df = 36.78) but causes (Ai) decreased duration (P = 0.003, t = 3.585, df = 36.98) and (Aii) increased number (P = 0.0003, t = 4.32, df = 35.14) of sleep bouts. (B) Kismet knockdown in PG with the R85G01-Gal4 driver (PG-Gal4 > UAS-kisRNAi-2, in red, n = 17) compared to background controls (PG-Gal4/+, in black, n = 13) does not alter the total amount of larval (second instar) sleep (P > 0.9, t = 0.178, df = 26.72), (Bi) average sleep bout duration (P > 0.9, t = 0.0186, df = 20.04) and (Bii) number (P = 0.7, t = 1.183, df = 25.44). Data are represented as means ± SEM. Two-tailed unpaired Welch’s t test with Bonferroni correction for multiple testing. P values are indicated as follows: **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001.
