Fig. 4. Binding pocket of allosteric modulators in CaSR.
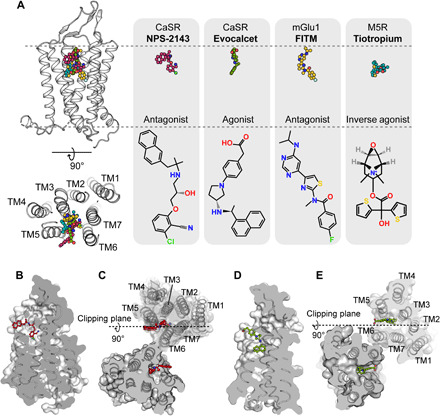
(A) Comparison of the similar binding pockets of the allosteric modulators in different GPCRs from a side view and an extracellular view. FITM in the mGlu1 structure (PDB code 4OR2) and tiotropium in the M5R structure (PDB code 6OL9) partially overlapped with the binding pocket of NPS-2143 and evocalcet in CaSR. Carbon atoms in the NPS-2143, evocalcet, FITM, and tiotropium models (upper row) are colored red, green, dark yellow, and cyan, respectively. Carbon atoms in the schematic drawing of NPS-2143, evocalcet, FITM, and tiotropium (bottom row) are shown in black. Nitrogen, oxygen, chloride, fluoride, and sulfide atoms are colored blue, red, light green, green, and yellow, respectively. (B and C) Cut-through surface side view of the NPS-2143 binding cavity in the protomer (B) and in the dimer (C) of the ggCaSR-NAM structure. NPS-2143 is represented as a ball-and-stick model. (D and E) Cut-through surface side view of the evocalcet binding cavity in the protomer (D) and in the dimer (E) of the ggCaSR-PAM structure. Evocalcet is represented as a ball-and-stick model.
