Fig. 3. Characterization of the biodegradation products of the PDLLA-Zn-nitrided Fe BRS after implantation in rabbit abdominal aortas.
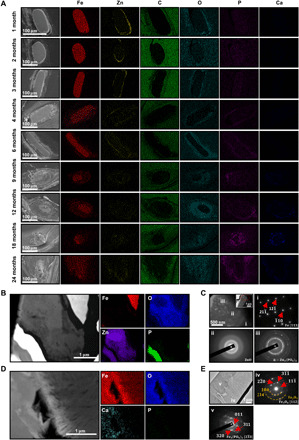
(A) Representative SEM images of the strut cross sections and the corresponding elemental distribution of the PDLLA-Zn-nitrided BRS 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, and 24 months postimplantation in rabbit abdominal aortas. (B) TEM image of the cross section of the PDLLA-Zn-nitrided Fe BRS strut and the corresponding elemental mapping 3 months postimplantation. (C) Morphology of the nanoscale Zn sacrificial layer region adjacent to the nitrided Fe platform and selected area electron diffraction (SAED) patterns of the marked regions (i) Fe, (ii) ZnO, and (iii) α − Zn3(PO4)2 3 months postimplantation. (D) TEM image of the cross section of the PDLLA-Zn–nitride Fe BRS strut and the corresponding elemental mapping 24 months postimplantation. (E) Morphology of the biodegradation products in the residual strut and the corresponding SAED patterns of the marked regions (iv) Fe3O4, Fe2O3, and (v) Fe3(PO4)2 24 months postimplantation.
