Fig. (4).
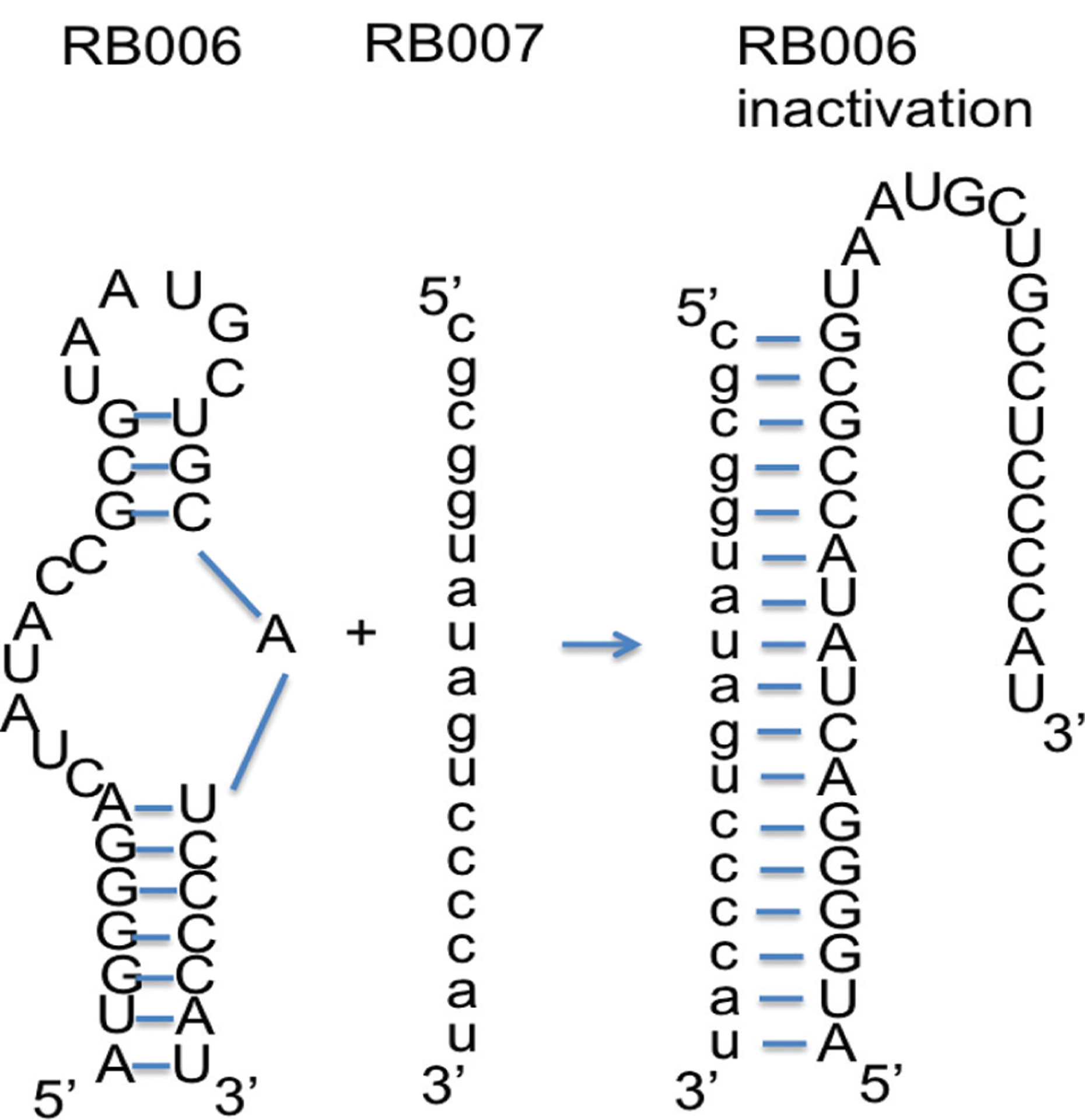
Aptamer-mediated anticoagulation during percutaneous coronary intervention and antidote-mediated control of factor IXa aptamer function. Utilizing Watson-Crick base-pairing rules, an antidote oligonucleotide (RB007) can be designed to interact with a portion of the factor IXa aptamer (RB006). Upon binding and unwinding the aptamer, the antidote converts the aptamer’s structure from a functional one to an inactive conformation thereby reversing the aptamer’s ability to inhibit factor IXa activity.
