TABLE.
Summary of Proteostasis Factors Valosin-Containing Protein (VCP), 26S Proteasome, Hsp104, and C9orf72 Role in Proteostasis, Their Substrates, and Mutation-Associated Diseases (PDB: 6OA9, 6MSD, 5VJH, 6LT0; EMDB: 7479)
| Proteostasis Factor | Role in Proteostasis | Associated Substrates | Mutation-Associated Diseases |
|---|---|---|---|
|
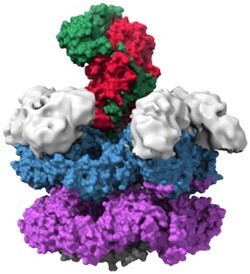
Valosin-containing protein
|
|
Tau, transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 kDa (TDP-43) | Vacuolar tauopathy, multisystem proteinopathy |
|
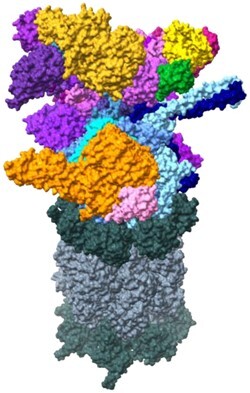
26S proteasome
|
|
Amyloid precursor protein, Tau, α-synuclein, polyQ aggregates, poly-GA aggregates | N/A |
|
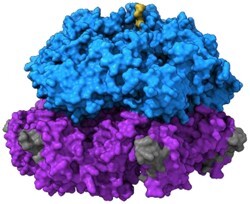
Hsp104
|
|
Seminal amyloid, TDP-43, α-synuclein, FUS, stress granules | N/A (yeast protein) |
|
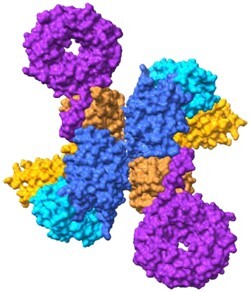
C9orf72
|
|
Rab8a, Rab11a, Arf1, Arf5, Arf6, 26S proteasome (binding partner with 65 other neurodegenerative associated proteins) | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, frontotemporal degeneration |