Fig. 4.
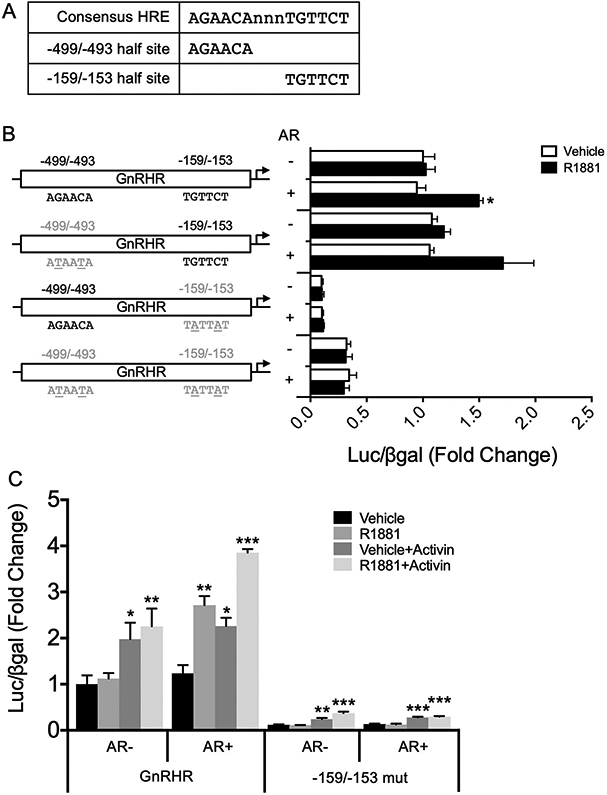
An HRE half site at −159/−153, but not −499/−493, is required for AR induction of GnRHR-luciferase. (A) Consensus HRE half sites identified at −499/−493 and −159/−153 within the mouse Gnrhr promoter, compared to a full-length consensus HRE. (B) Within the mouse −600 bp Gnrhr promoter driving luciferase, HRE half sites at −159/−153 and −499/−493 were mutated such that critical G and C residues were mutated to A or T residues. Mutated half sites are indicated by gray text, and the specific nucleotides mutated are underlined. LβT2 cells were transiently transfected with wildtype or mutant GnRHR-luciferase reporter constructs with empty vector or rAR. Cells were treated with vehicle control or 10−7 M R1881 for 24 h before harvest for luciferase and β-galactosidase assays. Data are represented as mean fold change relative to empty vector/vehicle/GnRHR-luc ± SEM for three independent experiments performed in triplicate. For each reporter, data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc analysis. Stars indicate significant results compared to empty vector/vehicle for each reporter. *, p < 0.05. (C) LβT2 cells were transiently transfected with wildtype or −159 mut GnRHR-luciferase with empty vector or rAR. Cells were treated with vehicle or 10−7 M R1881, with or without 10 ng/mL activin, for 24 h before harvest for luciferase and β-galactosidase assays. Data are represented as mean fold change relative to empty vector/vehicle/GnRHR-luc ± SEM for three independent experiments performed in triplicate. For each reporter, data were analyzed by multivariate ANOVA with Tukey post hoc analysis. Stars indicate significant results compared to empty vector/vehicle for each reporter. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
