Figure 2.
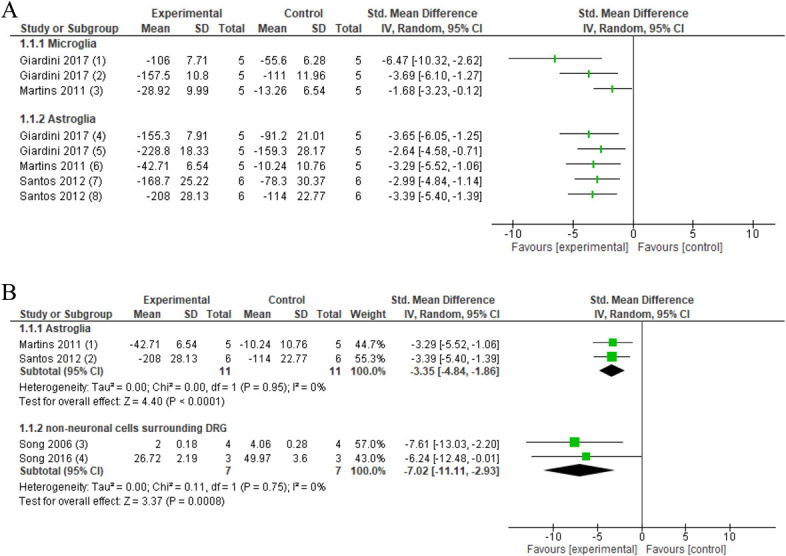
Forest plot for neuroinflammatory markers. 2A. Forest plot for microglia markers OX-42 and CD11b/c and astroglia marker GFAP. Favours experimental implies a reduction in microglia markers. (1) Number of OX-42 levels in PAG in the CCI model after several sessions of neural mobilisation (experimental) compared with no intervention (control). (2) Number of OX-42 levels in the thalamus in the CCI model after several sessions of neural mobilisation (experimental) compared with no intervention (control). (3) CD11b/c immunoreactivity in the spinal cord L4-5 in crush injury after several sessions of ankle mobilisation (experimental) compared with no intervention (control). Favours experimental implies a reduction in astrocyte GFAP. (4) GFAP protein levels in PAG in the CCI model after several sessions of neural mobilisation (experimental) compared with no intervention (control). (5) GFAP protein levels in the thalamus in the CCI model after several sessions of neural mobilisation (experimental) compared with no intervention (control). (6) GFAP immunoreactivity in the spinal cord L4-5 in crush injury after several sessions of ankle mobilisation (experimental) compared with no intervention (control). (7) GFAP protein levels in the spinal cord after several sessions neural mobilisation (experimental) compared with no intervention (control). (8) GFAP protein levels in DRG after several sessions neural mobilisation (experimental) compared with no intervention (control). 2B: Forest plot for GFAP and number of nonneuronal cells surrounding the DRG. Favours experimental implies that astrocyte marker GFAP in the spinal cord of these animal models of nerve injury is reduced after joint and nerve mobilisations (experimental) compared with no intervention (control). (1) GFAP immunoreactivity in the spinal cord L4-5 in crush injury after several sessions of ankle mobilisation (experimental) compared with no intervention (control). (2) GFAP protein levels in the spinal cord after several sessions of neural mobilisation (experimental) compared with no intervention (control). Favours experimental implies a reduction in the number of nonneuronal cells surrounding the DRG. (3) Number of nonneuronal cells surrounding DRG in intervertebral foramen inflammation. Activator-assisted spinal manipulation (ASMT; experimental) compared with no intervention (control). (4) Number of nonneuronal cells surrounding the DRG in compression–decompression of the dorsal root ganglion model after ASMT (experimental) compared with no intervention (control). CCI, chronic constriction injury; DRG, dorsal root ganglion; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein.
