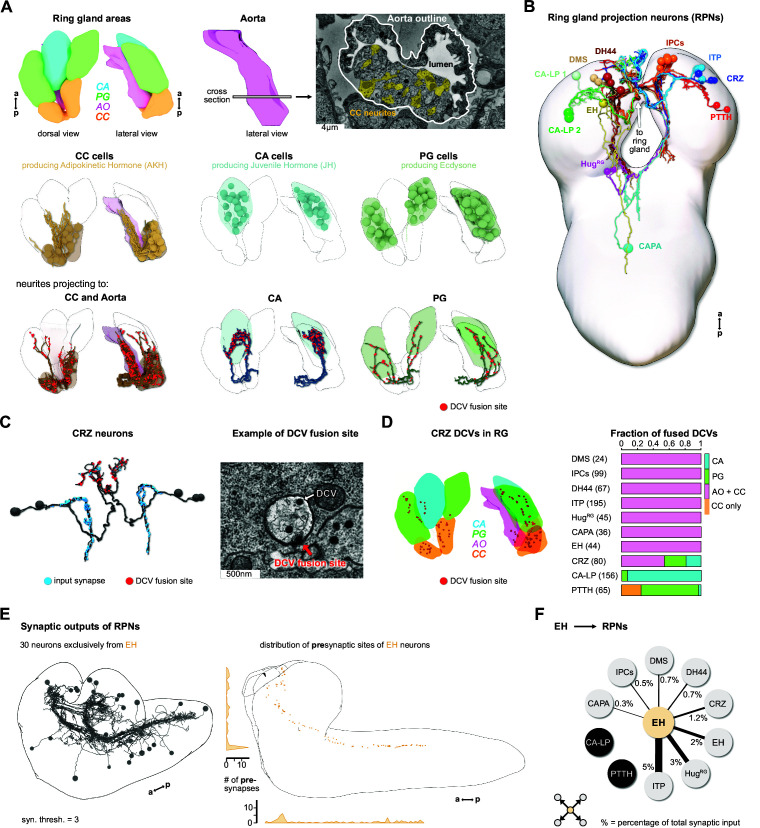
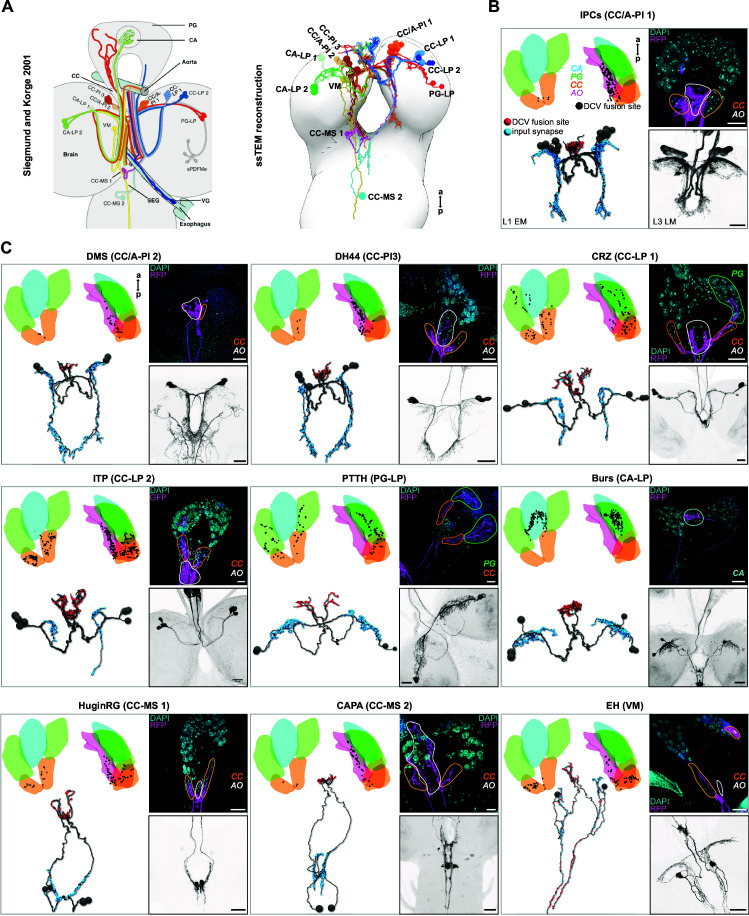
Figure 2. Reconstruction of the Drosophila larval ring gland and RPNs.
(A) Upper panel: 3D reconstructed RG areas in dorsal and lateral view (CC = orange, PG = green, CA = blue, AO = pink). Cross section of the AO: colored areas represent single neurites of different CC cells. Middle panel: dorsal and lateral view of the RG showing the different cells in the distinct RG areas (CC, CA, and PG). Lower panel: neurites innervating the RG areas were separated based on innervation of the CC and aorta, only CA or only PG. Fused DCVs are marked as red dots. (B) Schematic of all 56 neurons innervating the RG named by the main neuropeptide produced. Total number of neurons per RPN cluster: DMS = 4, IPCs = 14, DH44 = 6, CRZ = 6, ITP = 8, CA-LP = 6, PTTH = 4, HugRG = 4, CAPA = 2, EH = 2. For clarity, only one side is shown for each neuronal cluster. (C) Left: reconstructed CRZ. Fused DCVs were marked as non-polar output synapses at distal neurites in RG tissues (red dots). Blue dots represent chemical synaptic input sites. Right: example picture of a DCV fusion site in the EM volume (DCV has to be fused to the membrane). (D) Left: magnification of the reconstructed RG with spatial distribution of CRZ DCV fusion sites (red dots).Right: quantification of all DCV fusion sites found in the RG areas for each RPN group. Numbers in brackets are total numbers of marked DCVs. The X-axis represents a fraction of fused DCVs. (E) Left: synaptic outputs of all RPNs (threshold = 3 synapses) constitute in total 30 neurons, which are exclusively downstream of EH RPNs. Right: spatial distribution of presynaptic sites of EH. EH neurons are the only RPNs having presynaptic sites located along abdominal, thoracic segments, and SEZ and protocerebrum. (F) EH neurons synaptically target other RPNs. Percentage represents the fraction of input of distinct RPNs from EH neurons, for example, ITP neurons receive 5% of its inputs from EH. a: anterior; AO: aorta; CA: corpus allatum; CA-LP: corpus allatum innervating neurosecretory neurons of the lateral protocerebrum; CAPA: capability neurons; CC: corpora cardiaca; CRZ: corazonin neurons; DCVs: dense core vesicles; DH44: diuretic hormone 44 neurons; DMS: Drosophila myosuppressin neurons; EH: eclosion hormone neurons; HugRG: Hugin neurons innervating ring gland; IPCs: insulin-producing cells; ITP: ion transport peptide neurons; p: posterior; PG: prothoracic gland; PTTH: prothoracicotropic hormone neurons; RG: ring gland; RPN: ring gland projection neurons; SEZ: subesophageal zone; ssTEM: serial section transmission electron microscope.