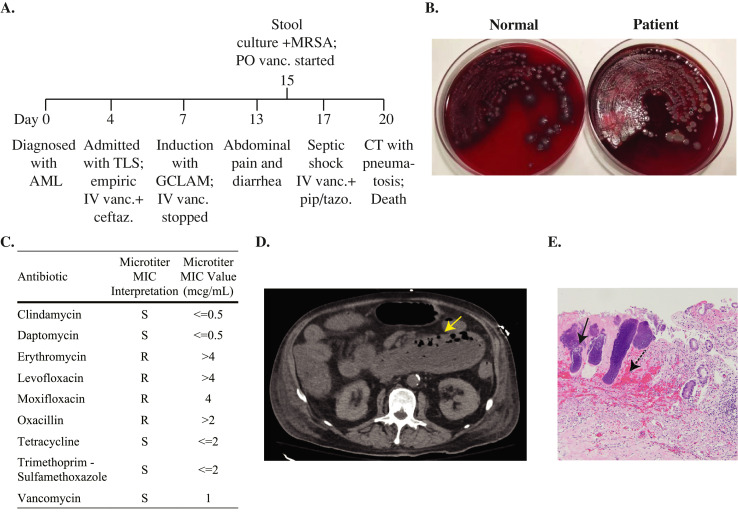
Fig. 1.
Clinical, microbiologic, radiographic, and histopathologic findings in a case of MRSA enterocolitis. (A) Timeline of the clinical course from diagnosis to death. (B) Stool cultures from a healthy individual (left) and from the patient (right) showing yellow colonies surrounded by hemolysis. (C) Antibiotic susceptibility testing of the Staphylococcus aureus isolate. (D) CT scan of the abdomen with the yellow arrow indicating an area of pneumatosis. (E) Postmortem histopathology of small bowel mucosa. The black arrow points to an area of Gram-positive cocci. The dotted arrow points to an area of submucosal necrosis and hemorrhage. Abbreviations: IV, intravenous; PO, oral; Vanc, vancomycin; Pip/tazo, piperacillin/tazobactam; MIC, minimum inhibitory concentration; AML, acute myeloid leukemia; CT, computed tomography; GCLAM, filgrastim, cladribine, cytarabine, and mitoxantrone; MIC, minimum inhibitory concentration; MRSA, methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus; TLS, tumor lysis syndrome.