Figure 2. Identify potential YAP target genes that regulate ferroptosis through integrated genomics.
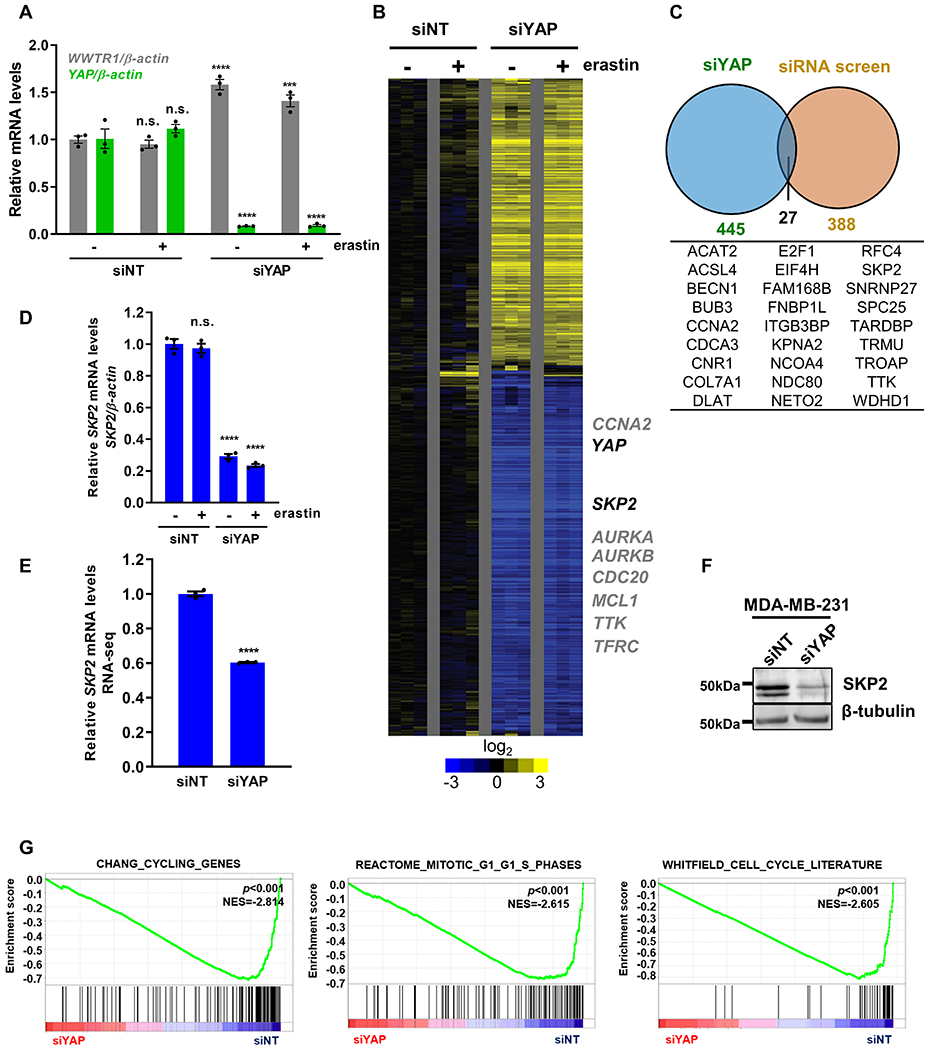
(A) The mRNA expression levels of YAP and WWTR1 (TAZ) were determined by RT-qPCR after siRNA-mediated YAP knockdown in RCC4 cells. n=3; mean ± SEM; one-way ANOVA; n.s.: not significant; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
(B) The heatmap of the transcriptome response of RCC4 cells to YAP knockdown without (-) or with (+) erastin treatment. n=3 per group.
(C) Venn diagram showing genes that were both downregulated upon YAP knockdown and identified as hits in the siRNA ferroptosis screen.
(D) RT-qPCR was used to validate the downregulation of SKP2 mRNA level upon YAP knockdown in RCC4 cells. n=3; mean ± SEM; one-way ANOVA; n.s.: not significant; ****p < 0.0001.
(E) RNA-seq revealed that SKP2 mRNA level was downregulated when YAP was knockdown in CAOV2 cells. n=3; mean ± SEM; Student’s t-test; ****p < 0.0001.
(F) Western blots validated that YAP knockdown decreased SKP2 protein level in MDA-MB-231 cells.
(G) GSEA analyses show the YAP knockdown in RCC4 cells led to the depletion of several cell cycle-related genesets.
